Sunlight or vitamin D or both? By Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Sunlight or vitamin D? That is a question that should not be necessary, yet many believe that vitamin D replaces sun exposure. So, they will state, “just take some vitamin D pills rather than go out in the sunlight, thus, you can derive sunlight benefits without the risk of skin cancer.” This opinion is incorrect, and it leads to sun deprivation.

This poor opinion of sunlight is misguided, erroneous and dangerous.
First of all, sunlight leads to production of many photoproducts when it touches the skin or enters the eyes. (Do not stare into the sun, since sufficient sun enters the eyes by reflection from objects or from the sky). These photoproducts include serotonin, endorphin, vitamin D, dopamine, brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) and nitric oxide.
Furthermore, all of these sunlight photoproducts are known to have healthful effects.
In addition, there are more photoproducts that are produced by sun exposure, but they have not yet been well-studied. Yet, it is likely that all of them will be found to have salubrious effects for the human body. Hence, we need them all. Obviously, a vitamin D pill cannot provide all the health benefits that sunlight provides.
Vitamin D in isolation may not always be healthful. Consider sunlight instead.
So yes, vitamin D is an important photoproduct of sunlight, but it is just one of the photoproducts. Thus, it is along for the ride with its companions. The serum blood tests which measure vitamin D are really surrogate measures for sunlight exposure and its other photoproducts. And, these photoproducts work as a team; one might say a “holistic” team.
Sunlight or vitamin D. What does the vitamin D research tell us?
A surprising piece of recent research assessed the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on bone strength and density. The researchers worked with 311 healthy volunteers aged 55 to 70 and these volunteers were split into three groups. One group received 400 international units (IU) per day of vitamin D, and a second group received 4,000 IU per day. Finally, a third group received 10,000 IU per day. Bone strength and density were measured at the beginning of the investigation and at intervals of 6, 12, 24 and 36 months. The researchers had thought there would be an increase in bone mass, yet, the results were opposite of their expectations. Stunningly, all three groups lost bone mass, and the higher the vitamin D dose, the more rapid the bone loss!
How can this happen? Does sunlight exposure play a part?
So, we have an interesting dichotomy here. First of all, we see that isolated vitamin D (the supplements) were counterproductive for bone strength and mass. And yet, we know that low serum levels of vitamin D are associated with low bone density. Maybe we can unravel this mystery by mentioning that almost all serum vitamin D (about 90%) is produced by sun exposure on the skin.
Therefore, low vitamin D levels are really indicative of sunlight deprivation.
And as aforementioned, one isolated chemical (vitamin D), cannot possibly be expected to take the place of the holistic sun. Especially relevant is a study that found Spanish women who sunbathed had 1/11 the fracture risk of indoor women. Is there any doubt that the strong-boned women had higher vitamin D levels than their counterparts? You see, we have gotten it backward, because greater sun exposure associates with higher vitamin D levels and predicts long life and health. Sunlight leads to vitamin D production, but vitamin D does not bring sunlight and all its additional photoproducts.
Does vitamin D supplementation protect against cardiovascular disease (CVD), or is it sunlight?
We know the answer to half of that that question due to a study of more than 83,000 people. And this study was a meta-analysis. This means a compilation and analysis of the best supplementation studies. The study compared vitamin D intake with CVD events (heart attacks, stoke, death from CVD and all-cause death). The authors found, as a result, that vitamin D supplementation was not associated with CVD.
Most noteworthy is that for years, sunlight was shown to associate to a much reduced risk of CVD.
And, that included heart attack and stroke.
Many made the mistake of giving the credit for the reduced risk to vitamin D, because of this research.The answer to health is to embrace the holistic sun and not a single photoproduct.
Sunlight related to the beta carotene study
This reminds me of research on beta-carotene, an antioxidant nutrient found in orange and yellow vegetables such as carrots. Since these vegetables have healthful properties, the researchers decided to experiment with isolated beta-carotene. They wanted determine if beta-carotene also had anti-cancer properties. To their dismay, these experiments associated to an increase in cancer. Does isolated vitamin D lead to the same deleterious outcomes? Sunlight should also be used in its whole form, just like the carrot.
So in the winter, in climes where there is little sunlight, how do we get our share of life-saving light?
The best method is to use a good sunbed (tanning bed), and when the sunlight is available, to be outside enjoying it, summer and winter. Sunbed use has many life-enhancing effects, including longer life, stronger bones and better mood. Read more about sunbeds, sunlight, bone strength and health at http://sunlightinstitute.org/ and read the book by Sorenson and Grant: Embrace the Sun.

Happy sunning! And remember never to burn.
Marc Sorenson, EdD, Sunlight Institute.
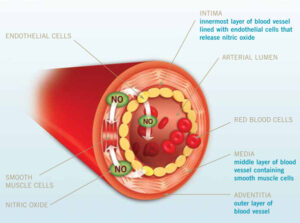
Anything that causes arterial plugging or prevents the relaxation of blood vessels can contribute to cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Poor diet, little exercise and lack of sunlight exposure form a combination that devastates vessel health and reduces the flexibility of those vessels. Among the CVD are ischemic heart disease, intermittent claudication (painful oxygen restriction to the legs), ischemia of the brain leading to strokes, peripheral artery disease and erectile dysfunction. Yes, I said erectile dysfunction.
ED is considered one of the major predictors of CVD.[i] It is caused by inability of the corpus cavernosa, two cylindrical chambers that run the length of the penis, to become engorged with blood, causing erection. When the process takes place normally, the cavernosa are stimulated by nitric oxide (NO), they then relax, and blood flows into the penis, allowing erection to take place. Therefore, erection is a vascular event.[ii] The same effect is seen in blood pressure decreases caused by NO after sunlight exposure. Ultraviolet A (UVA) light stimulation of the skin causes the release of NO from pre-formed stores of NO in the skin. NO is a potent vasodilator, and when it is released into the arteries by UVA stimulation, causes increased blood flow and lowers blood pressure.[iii] The mechanism is much the same in both instances. This is another example of sunlight enhancing health without the benefit of vitamin D. UVA light, that stimulates nitric oxide release, does not stimulate the skin to produce vitamin D.
An early study assessed the affect of ultraviolet light (UV) exposure to cavernosal strips, which were obtained from men during penile prosthetic surgery.[iv] The strips showed relaxation in response to UV, and the relaxation increased with the duration of exposure. We expect that sunbathing, which would profoundly increase NO in the circulation, would also vasodilate the cavernosa to allow erection. The same nitric oxide mechanism that lowers blood pressure, would seem to be a good method to treat ED. After all, drugs for ED, such as Viagra and Cialis, work by enhancing the effects of nitric oxide.[v] Sunlight is free and is a much better choice.
[i] Pastuszak AW, Hyman DA, Yadav N, Godoy G, Lipshultz LI, Araujo AB, Khera M. Erectile dysfunction as a marker for cardiovascular disease diagnosis and intervention: a cost analysis. J Sex Med 2015 Apr;12(4):975-84.
[ii] Marc Sorenson and William B. Grant. Does vitamin D deficiency contribute to erectile dysfunction? Dermatoendocrinol 2012 Apr 1; 4(2): 128–136.
[iii] Liu D, Fernandez BO, Hamilton A, Lang NN, Gallagher JM, Newby DE, Feelisch M, Weller RB. UVA irradiation of human skin vasodilates arterial vasculature and lowers blood pressure independently of nitric oxide synthase. J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jul;134(7):1839-46.
[iv] Kim SC, Oh CH, Park JK, Lee MY, Uhm DY. Effects of ultraviolet light on the tension of isolated human cavernosal smooth muscle from non-diabetic and diabetic impotent men. Urol Res. 1997;25(2):149-52.
[v] Mayo Clinic Online. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/erectile-dysfunction/in-depth/erectile-dysfunction/art-20047821. Accessed July 3, 2015.