 Should a bat sunbathe?
Should a bat sunbathe?
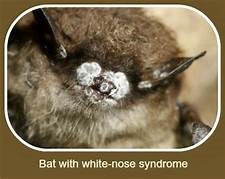
Last summer, while my friends and I were about to enter Lehman Caves, located in Nevada’s Great Basin National Park. A park ranger asked asked us if any of us had been in other caves anywhere in the U.S. The ranger said that although Lehman Caves had not yet been effected, there was a rapidly-spreading disease, suffered by cave-dwelling bats, which was decimating the bat population across the country. A fungus caused the disease that turned the bats’ noses white. Hence, it was accurately called “white nose syndrome.” None of our group had been in any caves in the recent past and therefore were pronounced clean. We then had a wonderful tour through a spectacular cave.
Sunbeds for bats?
This experience made a memorable impact on me. I recently discovered, to my surprise, that white-nose syndrome could be stopped by using sunbeds—bat sunbeds that is.[1] A spectrum of light emitted from both sunlight and sunbeds (UVB). UVB causes tanning and is also capable of damaging the DNA of the fungi that cause the disease, thereby destroying them. So, the treatment is to fit the bats’ cave entrances with UVB lamps. Researchers from the University of Wisconsin suggested this idea.
Sunbeds are anti-fungal.
Furthermore, this is not the first research to point out the anti-fungal nature of UVB light. Research has shown that sunlight may be good for decontaminating socks and feet, much as it decontaminates our bat friends. Scientists tested socks infected with the fungus causing tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot”), a chronic skin disease. The objective of the research was “to evaluate the effectivity of sun exposure in reducing fungal contamination in used clothing.” Fifty-two socks, proven by fungal culture to be contaminated by patients with tinea pedis, were studied. The samples were divided into two groups: Group A underwent sun exposure for 3 consecutive days. Group B remained indoors. Fungal cultures were performed at the end of each day.[2] It is most noteworthy that elimination of the fungal cultures was significant in the sun-exposure group, but not the indoor group.
When I was young, my mother washed our clothing and hung it on a clothesline. It had full exposure to sunlight. I won’t forget how fresh the clothing (including the socks) smelled after ward. I expect that as a result, any fungi or bacteria were eliminated, along with the resultant odor. Had the clothing remained inside it would have likely become malodorous.
In conclusion, the message is that both we and the bats can benefit from exposure to UVB light. It is especially relevant that bats are a vitally important part of the ecosystem; therefore we should protect them any way we can. Sun exposure and sunbed exposure, when used in a safe, non-burning manner, will help both the health and the environment. Safely embrace the sun!
[1] http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/bats-white-nose-syndrome-uv-treatment-fungus-1.4515314.
[2] Amichai B, Grunwald M, Davidovici B, Shemer A. Sun as a disinfectant. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014 Jul;16(7):431-3.
Stay slim with sun exposure?  New, never considered research adds a reason to stay active in the sun:[1] The blue-light spectrum of sunlight, a spectrum that can penetrate the skin, can cause subdermal fat tissue to decrease in size. In other words, it can cause fat loss. Thus, the action of sunlight may help one to stay slim or become slim. The researchers showed that daily exposure of differentiated adipocytes [fat cells] to blue light resulted in decreased lipid droplet size and increased basal lipolytic [fat breakdown] rate.
New, never considered research adds a reason to stay active in the sun:[1] The blue-light spectrum of sunlight, a spectrum that can penetrate the skin, can cause subdermal fat tissue to decrease in size. In other words, it can cause fat loss. Thus, the action of sunlight may help one to stay slim or become slim. The researchers showed that daily exposure of differentiated adipocytes [fat cells] to blue light resulted in decreased lipid droplet size and increased basal lipolytic [fat breakdown] rate.
The researchers had been doing research on light and diabetes, and they serendipitously found that the light could be an asset in maintaining (or producing) a slim body. But there are many other studies that show sun exposure is capable of assisting the body in being slim. For example: here is another benefit of sun exposure—morning sun specifically: A recent study from Northwestern Medicine demonstrates that timing and intensity of light correlate with body mass index (BMI).[2] BMI is a numerical computation comparing height and weight, and is a commonly used method to assess obesity or the lack thereof. A high BMI usually means a person is obese or at least approaching obesity, while optimal BMI is 18-25. Below 18 is considered underweight, above 25 is overweight, 30 is obese and 40 and above is morbidly obese. However, BMI does not work for heavily-muscled people, who may have minimal fat, but whose BMI puts them in an obese category—in reality, they are very slim.
This study showed that exposure to bright morning light was directly related to BMI. After adjusting for confounders such as diet, exercise and timing of sleep, it was determined that very early exposure to morning light correlated remarkably to lower BMI—they were slim, or at least slimmer. Even when light intensity was equal at different times of the day, those who received the earliest bright light had lower BMI. Most noteworthy was the fact that for each hour later in the day when light exposure occurred, BMI increased by 1.3 units. This fact is especially relevant, since a person who has a BMI of 25 (upper ideal range) could approach 30 (obesity), over time, due to the habit of receiving sun exposure later in the day, e.g. 10:00 AM rather than 6:00 AM.
The authors suggested that the mechanisms by which early light exposure could influence the “slim” mechanisms, could be the following: (1) resetting the circadian rhythm (internal clock), (2) the greater quantity of blue light in morning sun and (3) effects on melatonin production. Whatever the mechanisms, we now know that early-morning sun is important to being slim. In addition, it may also be important to other health issues. Rather than think of sun exposure as the cure-all for obesity, we must realize that poor nutritional habits and lack of exercise are much more important. Nevertheless, sun exposure can furnish one more arrow in the quiver.
Sun exposure is far superior to vitamin D supplements in preventing weight gain.
Another scientific paper “sheds more light” on the subject of being slim.[3] This research was conducted on mice with shaved backs that were placed on a high-fat diet and then exposed to non-burning ultraviolet radiation (UVR) during a three-month experiment. The mice, without the benefit of UVR, would have been expected to gain weight rapidly, but when they were exposed to UVR, the weight gain was impressively reduced. Furthermore, the UVR treatment achieved 30-40% less weight gain, compared to the expected weight gain with the high-fat diet. So, not only can sun exposure produce slim humans, it can help to produce slim rats.
Other benefits for the rats included: significant reductions in glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and fasting insulin levels (all markers and predictors of diabetes), nonalcoholic fatty liver disease measures and cholesterol. All of these factors, including obesity, are part of a cluster of maladies known as the metabolic syndrome, or MetS, which is indicative of deteriorating health and susceptibility to heart disease and diabetes. Finally, almost all people who have the aforementioned indications of MetS have a large problem maintaining slim bodies. Not a surprise, eh?
Other interesting findings:
Supplementation with vitamin D actually reduced the aforementioned beneficial effects. Dr. Shelley Gorman, one of the authors, made the following three interesting observations:[4]
- “These findings were independent of circulating vitamin D and could not be mimicked by vitamin D supplementation.”
- “It looked like the presence of vitamin D in mice on the high fat diet prevented the [beneficial] effect of UV radiation on weight gain.”
- She also mentioned the mechanism of weight loss may be dependent on nitric oxide (NO), which originates from diet and can be mobilized by UV radiation to become bioactive. This was due to the fact that in another part of the experiment, skin induction of nitric oxide (NO)—also a product of skin exposure to sun—reproduced many of the positive effects of UVR, something vitamin D supplements could not do.
The Authors conclusions:
The authors concluded their research thusly: These studies suggest UVR (sun exposure) may be an effective means of suppressing the development of obesity and MetS, through mechanisms independent of vitamin D but dependent on other UVR-induced mediators such as NO.”
It has been suggested that since low 25(OH)D levels correlate to obesity, those low levels are a possible cause of obesity. However, vitamin D is stored in fat tissue. Therefore, an increase in fat will lower the quantity of 25(OH)D circulating in the blood. Hence, low vitamin D is a consequence of obesity, and not the cause.[5]
Research continues to mount about the positive effects of sun exposure, independent of vitamin D production. This should in no way be construed to diminish the vital importance of vitamin D. Rather, it is to make a point that sun exposure works in many ways, including stimulating the production of vitamin D, NO, serotonin and endorphins. Why should we be satisfied with any one of these marvelous health aids when the sun is available? Because, with sun exposure, we can enjoy the benefits of the entire package.
So, being slim is dependent on a series of choices: avoiding junk food, eating large quantities of vegetables and fruits, taking a daily walk or engaging in other aerobic exercise, weight training and, finally, soaking up some daily, non-burning sunlight.
In conclusion: Stay slim, my friends.
[1] Katarina Ondrusova, Mohammad Fatehi , Amy Barr, Zofa Czarnecka, Wentong Long, Kunimasa Suzuki, Scott Campbell, Koenraad Philippaert, Matthew Hubert, Edward Tredget, Peter Kwan, Nicolas Touret, Martin Wabitsch, Kevin Y. Lee & Peter E. Light. Subcutaneous white adipocytes express a light sensitive signaling pathway mediated via a melanopsin/TRPC channel axis. Scientific Reports November 27;7:16332
[2] Reid KJ, Santostasi G, Baron KG, Wilson J, Kang J, Zee PC. Timing and intensity of light correlate with body weight in adults. PLoS One 2014;2;9(4)
[3] Geldenhuys S, Hart PH, Endersby R, Jacoby P, Feelisch M, Weller RB, Matthews V, Gorman S. Ultraviolet radiation suppresses obesity and symptoms of metabolic syndrome independently of vitamin D in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes. 2014 Nov;63(11):3759-69
[4] Dr. Shelly Gorman, quoted on Science Network Australia article: Sun shines light on obesity challenge. http://www.sciencewa.net.au/topics/health-a-medicine/item/3618-sun-shines-light-on-obesity-challenge (accessed February 4, 2016)
[5] Cândido FG, Bressan J. Vitamin D: link between osteoporosis, obesity, and diabetes? Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 17;15(4):6569-9.
 Although liver cancer is generally thought to be related to drinking, other factor such as obesity, HIV infection, smoking, diabetes, socioeconomic factors, drugs and others come into play. A recent study compared sun exposure to liver cancer and adjusted for the aforementioned factors. Sun exposure was shown to be a major factor in reducing the risk of the most prevalent and deadly liver cancer, called hepatocellular carcinoma.[1]
Although liver cancer is generally thought to be related to drinking, other factor such as obesity, HIV infection, smoking, diabetes, socioeconomic factors, drugs and others come into play. A recent study compared sun exposure to liver cancer and adjusted for the aforementioned factors. Sun exposure was shown to be a major factor in reducing the risk of the most prevalent and deadly liver cancer, called hepatocellular carcinoma.[1]
Major finding for liver cancer:
The subjects were divided into five groups, or quintiles, based on their sun exposure. In addition such factors as as outdoor activity, geographical residence, urban or rural settings, etc. were adjusted for.
Most noteworthy, was the fact that for each quintile of increasing sun exposure, there was a 17% decrease in the liver cancer risk.
A disappointment:
The only disappointing part to the study was this: The researchers assumed that the positive influence of sun exposure on liver cancer was due to vitamin D production. And, they may have been correct. Yet the sun causes the body to produce many other photoproducts. Due to the sun’s myriad effects, serotonin, endorphin, BDNF, nitric oxide, and dopamine are all increased. Therefore, it is impossible to know if vitamin D alone was the reason for the reduced risk of liver cancer. However, vitamin D undoubtedly played a large part in the positive results. And, there is a problem with giving vitamin D the credit without knowing for sure. People may believe, due to this research, that they need only to take a vitamin D supplement to receive all benefits of sunlight. Therefore, they can make very bad assumptions.
This is the first study on sun exposure and liver cancer.
Probably, this is the first research to show a link between liver cancer and inadequate sun exposure. However, there are indications that sun exposure is associated with a reduced risk of another liver ailment, called fatty liver disease.[2]
In conclusion, if you are a liver lover, you can love your liver by protecting it from liver cancer. Hence, you should obtain your share of unscreened, direct, non-burning sun exposure. Happy sunning!
[1] Trang VoPham, Kimberly A. Bertrand, Jian-Min Yuan, Rulla M. Tamimi, Jaime E. Hart,
and Francine Laden. Ambient ultraviolet radiation exposure and hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in the United States. Environmental Health (2017) 16:89.
[2] Gorman S, Black LJ, Feelisch M, Hart PH, Weller R. Can skin exposure to sun prevent liver inflammation? Nutrients 2015 May 5;7(5):3219-39.
First of all, let’s define IBD:
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are known as Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). UC is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by relapsing and remitting episodes of inflammation limited to the mucosal layer of the colon.[1] Crohn’s however, can involve any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly affects the small intestine or the colon, or both.[2]
New Italian Research
Research from Italy, published in December, 2017, shows that inadequate sun exposure is associated closely with IBD.[3] The researchers demonstrated that “Patients with IBD are significantly less exposed to sunlight then controls in our Mediterranean Country, often to an extent that may impair Vitamin D activation.” Consequently, they suggest that increased sun exposure may prove beneficial to patients.
Other research:
Furthermore, in a 12-year investigation of hundreds of thousands of IBD patients, the following was found: Hospitalizations and prolonged hospitalizations for both UC and CD were higher among those who had low sun exposure, compared to those with very high sun exposure.[4] In addition, the same relationship was shown between sun exposure, bowel surgeries and deaths: more surgeries were needed for those IBD patients who experienced the lowest sun exposure compared to those who had the highest sun exposure, and more deaths occurred among those with low exposure.
Does sun exposure help other diseases?
Furthermore, an interesting side note to the aforementioned investigation was the large number of non-IBD patients analyzed for sun exposure levels. Most noteworthy was the finding that the same relationship existed as with the IBD patients—low sun exposure was associated with prolonged hospitalizations and more deaths when compared with high exposure. Therefore, sun exposure saves lives, whether by decreasing IBD or preventing the myriad additional diseases that we have previously discussed.
In conclusion, if you have a painful feeling deep in your gut, take action: First of all, get a diagnosis. But do it while simultaneously increasing your safe, non-burning sun exposure. It may be just what the doctor ordered!
[1] Peppercorn M, Cheifetz, A, Rutgeerts P, Grover S. Definition, epidemiology, and risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/definition-epidemiology-and-risk-factors-in-inflammatory-bowel-disease.
[2] Web MD http://www.webmd.com/ibd-crohns-disease/crohns-disease/inflammatory-bowel-syndrome.
[3] Vernia P, Burrelli Scotti G, Dei Giudici A, Chiappini A, Cannizzaro S, Afferri MT, de Carolis A. Inadequate Sunlight Exposure in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Dig Dis. 2017 Dec 18. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12567. [Epub ahead of print]
[4] Limketkai BN, Bayless TM, Brant SR, Hutfless SM. Lower regional and temporal ultraviolet exposure is associated with increased rates and severity of inflammatory bowel disease hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Sep;40(5):508-17.
 Does cognitive loss lead to dementia? Yes. Is vitamin D important to the risk of cognitive loss? Yes. Do those levels also influence the ability to think (cognitive ability)? In 2002, 252 people were assessed for vitamin D levels, signs of dementia and cognitive ability.[1] And, in 2012 another assessment was completed. The data was then assessed to determine if the initial vitamin D levels were associated with different risks of dementia and cognitive ability after 10 years.
Does cognitive loss lead to dementia? Yes. Is vitamin D important to the risk of cognitive loss? Yes. Do those levels also influence the ability to think (cognitive ability)? In 2002, 252 people were assessed for vitamin D levels, signs of dementia and cognitive ability.[1] And, in 2012 another assessment was completed. The data was then assessed to determine if the initial vitamin D levels were associated with different risks of dementia and cognitive ability after 10 years.
Cognitive ability results:
First of all, those with higher vitamin D levels at the beginning of the ten-year period had about 40% better executive functioning at the end of the period compared with those who had lower vitamin D levels (executive functions are a set of processes that all have to do with managing oneself and one’s resources in order to achieve a goal, and they can be viewed as the “conductor” of all cognitive skills.)[2]
Of course, vitamin D levels are determined by the quantity of sun exposure one receives. Therefore, we could say that vitamin D levels are a surrogate measurement of sun exposure.
Other research on sunlight and cognitive ability:Much research has been done on the association of sun exposure on cognitive abilities, so this research is no surprise. Especially relevant are the results of more recent research, based on a 15-year residential history of varying degrees of sun exposure. It has also shown cognitive impairment in persons who were below the median exposure to sun was 88% greater than those who were above the median.[3] Researchers mentioned vitamin D as a possible mechanism by which sun positively influenced cognitive abilities. And, they also remarked that regulation of the circadian rhythm by sun could be a factor. Additionally, these same investigators had previously shown the following: lower levels of sun exposure resulted in a 2.6-times higher incidence of cognitive impairment.[4]
Does BDNF play a part in protecting cognitive ability?
Part of the reason for better cognitive skills under the influence of sun exposure may not have anything to do with vitamin D. It could be due to a chemical called Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). It is a part of a cascade of proteins promoting growth of neurons and preventing nerve death.[5] It is especially relevant that BDNF levels have been shown to increase significantly after bright light exposure.[6] And, in what I would consider to be a remarkably important study, both light exposure and treadmill exercise increased the expression of BDNF in rats.[7] And—as the researchers showed—exercise and/or bright light promoted neurogenesis (new nerve cell growth) in the adult rat brain. How important is this finding for adults who are worried about cognitive decline? Furthermore, we are actually seeing an example of new brain cells being built by bright light and exercise! Researchers have shown that BDNF has an effect on behavior, mood (e.g. depression), and brain adaptation (e.g. plasticity) and that its levels fluctuate seasonally in correlation with the amount of ambient sun:[8]
In addition, we can add one more natural chemical inversely associated with cognitive decline, depression, memory loss, and nervous system degeneration, and directly associated with sun exposure. We now have vitamin D, serotonin, endorphins, dopamine and BDNF. Hence, sun exposure is absolutely necessary to human health. Be sure you are obtaining your share! Don’t let your mind deteriorate due to avoiding the sunlight.
Embrace the sun, but do it safely. Finally: avoid sunburn.
[1] Alicia M. Goodwill, Stephen Campbell, Steven Simpson Jr, Maria Bisignano,
Cherie Chiang, Lorraine Dennerstein, Cassandra Szoekea. Vitamin D status is associated with executive function a decade later: Data from the Women’s Healthy Ageing Project. Maturitas 107 (2018) 56–62
[2] http://www.ldonline.org/article/29122
[3] Kent ST, Kabagambe EK, Wadley VG, Howard VJ, Crosson WL, Al-Hamdan MZ, Judd SE, Peace F, McClure LA. The relationship between long-term sun radiation and cognitive decline in the REGARDS cohort study. Int J Biometeorol. 2014 Apr;58(3):361-70.
[4] Kent ST, McClure LA, Crosson WL, Arnett DK, Wadley VG, Sathiakumar N. Effect of sun exposure on cognitive function among depressed and non-depressed participants: a REGARDS cross-sectional study. Environ Health. 2009 Jul 28;8:34
[5] http://scicurious.scientopia.org/2010/12/13/bdnf-and-depression/
[6] Tirassa P1, Iannitelli A, Sornelli F, Cirulli F, Mazza M, Calza A, Alleva E, Branchi I, Aloe L, Bersani G, Pacitti F. Daily serum and salivary BDNF levels correlate with morning-evening personality type in women and are affected by light therapy. Riv Psichiatr. 2012 Nov-Dec;47(6):527-34.
[7] Kwon SJ, Park J, Park SY, Song KS, Jung ST, Jung SB, Park IR, Choi WS, Kwon SO. Low-intensity treadmill exercise and/or bright light promote neurogenesis in adult rat brain. Neural Regen Res. 2013 Apr 5;8(10):922-9.
[8] Molendijk ML, Haffmans JP, Bus BA, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW, Prickaerts J, Oude Voshaar RC, Elzinga BM. Serum BDNF concentrations show strong seasonal variation and correlations with the amount of ambient sun. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48046.
 Blood pressure is determined by (1) the amount of blood the heart pumps and the amount of resistance to blood flow in the arteries. Consequently, the more blood the heart pumps, and the tighter the arteries, the higher the blood pressure.[1]
Blood pressure is determined by (1) the amount of blood the heart pumps and the amount of resistance to blood flow in the arteries. Consequently, the more blood the heart pumps, and the tighter the arteries, the higher the blood pressure.[1]
Chronic high blood pressure, or hypertension, can damage arterial walls and can eventually lead to an increased risk from heart disease, heart failure, other arterial diseases, kidney disease, irregular heart rhythms, osteoporosis, cognitive dysfunction, painful intercourse and stroke.[2] High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is rampant in western societies. Untreated high blood pressure is a major killer. It is especially dangerous because it is primary risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
I have written several blogs on high blood pressure. Nevertheless, the experience of my friend Wayne may provide impetus for hypertension sufferers to try the sunshine solution.
Wayne, a resident of Texas, came to our former health resort seeking help for conditions of high blood pressure, obesity and various other maladies. I recommended, along with our healthful nutrition program, that he should sunbathe daily. Consequently, he “took it to heart” and could be found outside by the pool daily, dutifully soaking up the midday sunlight.
Wayne arrived at our program with a blood pressure of 157 systolic and 97 diastolic (157/97). Most noteworthy, those numbers put him at high risk for a stroke. Normal blood pressures are considered below 120 systolic, and below 80 diastolic. Four weeks later, as a result of his lifestyle changes. His numbers dropped to 125/54, meaning that he progressed from high stroke risk to very low stroke risk. Especially relevant is the fact that these changes were accomplished without medication.
The average drop in blood pressure among all guests at that program was 16 systolic and 12 diastolic. This is remarkable, considering that many of them had normal levels coming in.
Here are just a few of the blood pressure changes accomplished during that time:
- Frieda, from Oregon, lowered her blood pressure 33 points systolic and 30 points diastolic.
- Joyce, from Rhode Island, lowered her blood pressure 31 points systolic and 24 points diastolic.
- Jeff, from Utah, lowered his blood pressure 39 points systolic and 12 points diastolic.
- Susan, from New York, lowered her blood pressure 20 points systolic and 26 points diastolic.
Was all of this success due to sun exposure?
It should not be construed that these results were all a result of sun exposure. Nor should we conclude that hypertension is a result of sun deprivation. Typical American citizens engage daily in “killer” nutrition, subjecting themselves to dietary patterns and chemical additives that never existed in human life until modern times. Therein lie the major causes of hypertension. Hence, part of the improvements in blood pressure were due to the dietary changes we implemented with our guests.
More research regarding sunlight and blood pressure:
Sun exposure can, to an extent, act as an antidote to the poisons we consume. And, it acts much more quickly than dietary changes. Consider this: Dr. Oplander and his colleagues demonstrated that whole-body Ultraviolet A (UVA) irradiation worked what seemed like a miracle.[3] It caused a rapid, significant decrease of 11% in both systolic (upper number) and diastolic (lower number) blood pressure 30 minutes after the exposure. That change lasted up to 60 minutes. The lowered blood pressure lasted up to 60 minutes. Not only did blood pressure decrease, but arterial blood flow increased by 68%.
Nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator (blood-vessel relaxer) that occurs with sun exposure, was the photoproduct that led to these spectacular, important changes. This is important, because UVA is available almost any time the sun shines, winter and summer. Ultraviolet B (UVB) is not available in some areas during winter, due to the sun’s angle. This is especially true in the higher latitudes of the Northern hemisphere, or in the lower latitudes of the Southern hemisphere. UVB stimulates the production of vitamin D. So, it is especially relevant here that vitamin D was not involved in the lowering of blood pressure in Dr. Oplander’s study. Nitric oxide, however, was very involved.
Let’s take a look at one more study of sun exposure and hypertension: research China demonstrates that exposure to sun correlates to a lowered risk:[4] In a randomly selected population of Chinese residents from Macau (where the rate of hypertension is very high), the following risk factors for hypertension were assessed: lack of sun exposure, low intake of fish, smoking, obesity and lack of exercise. An average of more than one-half hour of sun exposure per day, as compared to no sun exposure, predicted a 40% reduced risk for hypertension.
I could go on for another page about the horrors of blood-pressure medication, but what I have said suffices. Non-burning sun exposure is one of the best elixirs for hypertension. In conclusion, one might say that it is no wonder that Wayne overcame his blood pressure problem!
[1] Mayo Clinic Diseases and Conditions: High blood pressure (hypertension). http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/basics/definition/con-20019580 (accessed January 5, 2016).
[2] Ann Pietrangelo. Healthline 2014 http://www.healthline.com/health/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/effect-on-body (accessed January 4, 2016).
[3] Opländer C, Volkmar CM, Paunel-Görgülü A, van Faassen EE, Heiss C, Kelm M, Halmer D, Mürtz M, Pallua N, Suschek CV.. Whole body UVA irradiation lowers systemic blood pressure by release of nitric oxide from intracutaneous photolabile nitric oxide derivates. Circ Res. 2009;105:1031–40.
[4] Ke L, Ho J, Feng J, Mpofu E, Dibley MJ, Feng X, Van F, Leong S, Lau W, Lueng P, Kowk C, Li Y, Mason RS, Brock KE. Modifiable risk factors including sun exposure and fish consumption are associated with risk of hypertension in a large representative population from Macau. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013 Nov 1 [Epub ahead of print].
 Bipolar disorder, or bipolar depression, may lead to early death. It is a mental condition characterized by alternating mania and depression, usually interspersed with normal mood. And, it also may include psychosis. Because of the alternating moods, bipolar disorder was previously called manic-depressive illness. The word “manic” means excessive activity, euphoric mood, and impaired judgement.
Bipolar disorder, or bipolar depression, may lead to early death. It is a mental condition characterized by alternating mania and depression, usually interspersed with normal mood. And, it also may include psychosis. Because of the alternating moods, bipolar disorder was previously called manic-depressive illness. The word “manic” means excessive activity, euphoric mood, and impaired judgement.
Bipolar disorder affects about 5.7 million adult Americans, and one in 5 people who have the condition commits suicide. Furthermore, the U.S. has the highest bipolar rate in the world.[1] Bipolar disorder is also the sixth leading cause of disability in the world. In addition, it results in a 9.2-year reduction in the expected life span.[2]
New (and very exciting) research demonstrates that bright-light therapy has a profound and positive influence on this disease.[3] The researchers conducted a 6-week program to investigate the value of bright light therapy at midday for bipolar depression. The study participants were chosen from depressed adults who were receiving stable dosages of anti-manic medication. The subjects were randomly assigned to treatment in one of two groups: the bright-white light (7,000 lux) group or dim-red light (50 lux) group.
At the end of the six-week period, 68% of the bright-light group went into remission of their bipolar problems, compared with 15% of the dim-light group. This is a most noteworthy result.
The study provides transcendently important information for those who suffer from this debilitating mental disorder. Therefore, the researchers summarized their findings thusly: “The data from this study provide robust evidence that supports the efficacy of midday bright light therapy for bipolar depression.”
The mechanism by which bright-light therapy performs its anti-depressive miracles is probably through production of serotonin in the brain. When we are surrounded by bright light, the light enters the eye and stimulates the brain to produce serotonin. Serotonin is the master mood enhancer, and anti-depressant drugs work by manipulating serotonin. Hence, these drugs are called selective serotonin uptake inhibitors (SSRI). However, SSRI often have serious, sometimes deadly, side effects. We should therefore obtain our serotonin naturally, through regular sun exposure. Why? Because serotonin can be increased by as much as 800% by spending a day in the sunlight.[4] What a marvelously simple therapy bright light is. And what is the easiest way to obtain it? Go outside during the day, for goodness sake!
It is not necessary to go outside at midday. Any time of day, when the sun is shining brightly, should work very well. However, we should never look directly at the sun. That may cause eye damage. Sufficient light enters just by being outside.
In conclusion: Safely embrace the sunlight whenever possible, and remove the risk of bipolar disorder.
[1] Amanda Gardner. U.S. has highest bipolar rate in 11-nation study. Heath.com. March 7, 2011. http://www.cnn.com/2011/HEALTH/03/07/US.highest.bipolar.rates/
[2] Bipolar Disorder Statistics. BDS Alliance. http://www.dbsalliance.org/site/PageServer?pagename=education_statistics_bipolar_disorder.
[3] Sit DK, McGowan J, Wiltrout C, Diler RS, Dills JJ, Luther J, Yang A, Ciolino JD, Seltman H, Wisniewski SR, Terman M, Wisner KL. Adjunctive Bright Light Therapy for Bipolar Depression: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2017 Oct 3: [Epub ahead of print].
[4] Lambert GW, Reid C, Kaye DM, Jennings GL, Esler MD. Effect of sun and season on serotonin turnover in the brain. Lancet. 2002 Dec 7;360(9348):1840-2.
Osteoarthritis is also known as wear-and-tear arthritis. Yet, the disease is not common in parts to the world where people work hard with their joints to make a living. Rather, the disease is relatively rare. Thus, we would not consider too much work to be the cause. One would think that all of that work with the joints would lead to more wear and tear, no? Osteoarthritis is characterized by bone and cartilage degeneration in joints. This leads to pain and joint stiffness and can lead to disability. 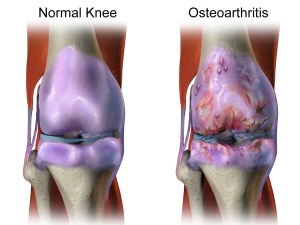
Vitamin D research.
Research has shown that those whose blood vitamin D measurements were in the middle and lowest thirds of serum vitamin D levels, had a threefold progression of osteoarthritis of the knee during a one-to-two year period. That is, when compared to those in the highest third. Low blood levels of vitamin D also predicted greater loss of cartilage in the joints.[1]
Other research demonstrates that in patients with arthritis of the knee, those with blood levels of vitamin D lower than 20 ng/ml (very low) have more disability. They also have more pain and more weakness than those with higher levels.[2], [3] Low vitamin D levels also correlate closely to greater knee pain and walking difficulty.[4]
Remember, unless it is stated that 25(OH)D levels are a result of supplementation or dietary sources, those levels are dependent on sun exposure. The research on osteoarthritis, discussed above, therefore, is really research on sun exposure.
Another horrific effect of arthritis.
Arthritic joints carry another devastating side effect. Hip replacement surgery is often prescribed for arthritic conditions: those people who go through total-hip-replacement procedures are 4.7 times as likely to have an ischemic stroke. They are also 4.4 times as likely to have a hemorrhagic stroke in the first two weeks post surgery.[5] Those stroke risks remain elevated for 6-12 weeks. The term “ischemic” means producing a local deficiency of blood supply by obstructing blood flow.
Sun exposure, therefore, has a protective effect against arthritis. Consequently, it has the potential to prevent hip-replacement surgery. In addition, it has the potential to prevent strokes.
Consider an article from the Express,[6] a UK online newspaper. It describes research published in the scientific journal, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases,[7]stating the following: “Millions of people could protect themselves from crippling arthritis by getting a regular dose of sunshine. Scientists found that women with the highest levels of exposure to the sun – specifically Ultraviolet B (UVB) light – were 21 per cent less likely to develop the disease.”
Safely embrace the sun, help prevent osteoarthritis and safeguard your health.
[1] McAlindonTE, Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Aliabadi P, Weissman B, Rush D, Wilson PW, Jacques P. Relation of dietary intake and serum levels of vitamin D to progression of osteoarthritis of the knee among participants in the Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med 1996;125:353-9.
[2] Baker K, Zhang YQ, Goggins J. Hypovitaminosis D and its association with muscle strength, pain and physical function in knee osteoarthritis (OA): a 30-month longitudinal, observational study; American College of Rheumatology meeting; San Antonio, TX; Oct 16-21, 2004; abstract 17552. Also see http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/538061
[3] Baker K, Zhang YQ, Goggins J. Hypovitaminosis D and its association with muscle strength, pain and physical function in knee osteoarthritis (OA): a 30-month longitudinal, observational study; American College of Rheumatology meeting; San Antonio, TX; Oct 16-21, 2004; abstract 17552. Also see http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/538061
[4] Wang, J., Nuite, M., Wheeler, L.M., Badiani, P., Joas, J., Mcadams, E.L., Fletcher, J., Lavalley, M.P., Dawson-Hughes, B., Mcalindon, T.E. 2007. Low Vitamin D levels are associated with greater pain and slow walking speed in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA). In: American College of Rheumatology Scientific Meeting, 11/6/07-11/11/07, Boston, MA. 56(9supplement): S124. Accessed May 14, 2010 at http://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publications.htm?SEQ_NO_115=211611
[5] Lalmohamed A, Vestergaard P, Cooper C, de Boer A, Leufkens HG, van StaaTP, de Vries F. Hip replacement surgery and stroke. Stroke 2012;43(12):3225-9.
[6] http://www.express.co.uk/life-style/health/375632/Sun-helps-stop-arthritis. (accessed November 27, 2015).
[7] Arkema EV, Hart JE, Bertrand KA, Laden F, Grodstein F, Rosner BA, Karlson EW, Costenbader KH. Exposure to ultraviolet-B and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women in the Nurses’ Health Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Apr;72(4):506-11
Recent research enlightened me to a paradox in cholesterol research. It appears that vitamin D supplementation actually raises total cholesterol (TC) levels and “bad cholesterol” levels (LDL). Supplementation is also associated with a small rise in “good cholesterol” levels (HDL). The paradox lies in the fact that sunlight exposure is associated with a decrease in total cholesterol levels and LDL, while also producing a small rise in HDL. In both cases, vitamin D levels are raised significantly. 
The research, from India, was born of a concern that although India has abundant sunshine, vitamin D deficiency is common, because so many do not take advantage of sunlight exposure. The researchers decided to determine whether it was better to use sunlight exposure to increase vitamin D levels, or to instead use vitamin D supplementation. To do this, they formed three groups: a control group that had “normal” levels above 50 nmoL (20 ng/ml), and two vitamin D-deficient group with levels below 50 nmoL. One of the vitamin D-deficient groups increased their usual sunlight exposure by at least 20 minutes to their face and arms between 11 AM and 3 PM daily. The other deficient group received oral supplements of 1,000 IU of vitamin D (cholecalciferol), but did not increase sunlight exposure. The researchers also measured cholesterol levels. The study lasted for 6 months and the results were as described above: A decrease in TC level and LDL levels in the sunlight exposure group, an increase in TC and LDL in the supplementation group, and an increase in HDL in both groups.
It would have been interesting if the subjects in the sunlight-exposure group had experienced full-body exposure for 20 minutes, which can produce up to 20,000 IU of vitamin D; a few minutes on the face and arms is not sufficient to optimize vitamin D levels. Equally, the use of 1,000 IU daily of vitamin D is miniscule. I would have suggested at least 4,000 IU daily. Altering upward the dosages of both sunlight and vitamin D could have shown larger differences. More research needs to be done to determine whether or not these results can be replicated.
The indications of this study is that vitamin D supplementation may be harmful because it raises serum lipids in an adverse manner. There is also an indication that sunlight exposure improves lipid profiles while still raising vitamin D levels.
By what mechanism would sun exposure lower cholesterol levels? A type of cholesterol precursor called 7-DHC is stored in the skin. It is also used to produce vitamin D when under the influence of sunlight. Regular sunlight exposure would reduce this cholesterol store and thereby reduce cholesterol levels.
As to why vitamin D supplementation might increase cholesterol levels, it could be due to the fact that it is usually made by radiating lanolin from sheep. Animal products are known to raise cholesterol levels.
Whatever the reasons for the ability of sunlight to lower cholesterol levels, this study is one more indication that sunlight is a friend to nearly every system of the body. Be sure to obtain plenty of non-burning sunlight. Your heart and brain will thank you for it!
 New research from New Zealand shows that children who live in South Island of New Zealand have at least three times the risk of bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC)[1] when compared to those who live on the North Island. According to an article referencing this research, these bowel diseases usually appear in the pre-teen or teenage years and are incurable. The researchers believe that sun exposure and one of its photoproducts, Vitamin D, may play a part, although the low selenium content of the soil may also have an influence on bowel diseases.
New research from New Zealand shows that children who live in South Island of New Zealand have at least three times the risk of bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC)[1] when compared to those who live on the North Island. According to an article referencing this research, these bowel diseases usually appear in the pre-teen or teenage years and are incurable. The researchers believe that sun exposure and one of its photoproducts, Vitamin D, may play a part, although the low selenium content of the soil may also have an influence on bowel diseases.
In the southern hemisphere, of course, the farther south one travels, the colder and cloudier the weather becomes. Hence, the South Island has far less sun exposure than the North Island.
Although the researchers did not know for sure that the sunlight and vitamin D hypothesis was correct regarding bowel disease, their idea certainly has plenty to back it up. Crohn’s disease is closely correlated to vitamin D deficiency and winter season,[2] indicating an inverse relationship with sun exposure and vitamin D production. A study of female nurses in the US found that “compared with women residing in northern latitudes [in the northern hemisphere] at age 30, the multivariate-adjusted risk for UC for women residing in southern latitudes was less than half.”[3] Also, in a 12-year investigation of hundreds of thousands of bowel disease patients, hospitalizations, and prolonged hospitalizations, for both UC and CD were higher among those who had low sun exposure compared to those with very high sun exposure.[4]
It is important to understand that bowel disease causes malabsorption of nutrients in the gut, leading to diseases of malnutrition.[5] Vitamin D is one of the “nutrients” that may not be absorbed efficiently, and therefore sun exposure, not supplements, may be the only viable source of vitamin D for a person with bowel disease.
So for a healthy gut, sun exposure plays a vital role. Be sure to enjoy safe, non burning sun exposure whenever possible.
[1] http://www.radionz.co.nz/news/national/340048/shining-light-on-bowel-disease-rates
[2] Gilman J, Shanahan F, Cashman KD. Determinants of vitamin D status in adult Crohn’s disease patients, with particular emphasis on supplemental vitamin D use. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jul;60(7):889-96.
[3] Khalili H, Huang ES, Ananthakrishnan AN, Higuchi L, Richter JM, Fuchs CS, Chan AT. Geographical variation and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among US women. Gut. 2012 Dec;61(12):1686-92.
[4] Limketkai BN, Bayless TM, Brant SR, Hutfless SM. Lower regional and temporal ultraviolet exposure is associated with increased rates and severity of inflammatory bowel disease hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Sep;40(5):508-17.
[5] Margulies SL, Kurian D, Elliott MS, Han Z. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with intestinal malabsorption syndromes–think in and outside the gut. J Dig Dis. 2015 Nov;16(11):617-33.
