Insufficient sunlight associates in a dose-response manner to higher risk of hypertension and earlier death. By Marc Sorenson, EdD. 
Understanding hypertension
Hypertension, or chronic high blood pressure, depends on the amount of blood the heart pumps and resistance to arterial blood. Thus, the tighter the arteries, the higher the blood pressure. The top number on a blood-pressure measurement, and stated in millimeters of mercury (mm/Hg), is systolic pressure. In addition, the lower number is diastolic pressure, another critically important measurement. Hypertension occurs when blood pressure is greater than 140/90 mm/Hg. Thirty-one percent of US adults are hypertensive. Hypertension can damage arterial walls and can eventually lead to an increased risk of death from heart disease, heart failure, and other arterial diseases. It also associates to a higher risk of kidney disease, irregular heart rhythms, osteoporosis, cognitive dysfunction, painful intercourse and stroke.
Does insufficient sunlight exposure influence hypertension?
Conventional textbook theory holds that the brain, blood vessels, and kidney regulate blood pressure. However, recent evidence suggests that the skin could also regulate hypertension, and insufficient sunlight plays a role in increasing it.
Insufficient sunlight, as mentioned, leads to a spate of diseases and disorders. In addition, some of those diseases have a dose-response relationship with sun exposure.
Hypertension is one of those diseases and can lead to disability and death. Blood pressure between 80 (diastolic pressure or lowest pressure) and 120 systolic (higher pressure), is in normal ranges. When blood pressure rises substantially above either of these figures and stays elevated, it is a danger signal.
Understanding the dose-response relationship.
So, what is a dose-response relationship (DRR)? This is where changes in one measured factor produces a predictable, consistent change in another measured factor. Thus, if I increase my exercise a certain amount weekly, I probably hope for a dose-response outcome: predictably better endurance. Consequently, if my body increases its endurance each week, my exercise produces a dose response relationship with endurance. Conversely, if someone stops exercising and loses a predictable amount of endurance, this is also a DRR (negative DRR).
An illustrative example of positive sunlight (rather than insufficient sunlight) and DRR.
My friend Wayne had severe hypertension when checking in at our former resort. After sunbathing each day for a month, hypertension decreased profoundly.
Wayne arrived with blood pressure of 157 systolic and 97 diastolic (157/97). Both of these measurements are dangerously high. Four weeks later, without medication, and while taking no vitamin D, the numbers dropped to 125/54. He had progressed from very high stroke risk to very low stroke risk. In addition, his vitamin D levels climbed to 103 ng/ml, a number I considered impossible without supplementation. I learned much, especially about sunlight, vitamin D levels and hypertension. Sufficient sunlight is a key to optimal levels of blood pressure. Many people believe that older persons cannot raise vitamin D levels. Yet, Wayne was in his seventies. Furthermore, insufficient sunlight was obviously a major cause of his hypertension. Wayne’s DRR occurred with the increased sun exposure and produced optimal blood pressure.
The latest research regarding insufficient sun exposure and hypertension
This latest research on insufficient sun exposure began by noting another important, but misleading fact. An inverse association exists between cardiovascular disease (CVD) and vitamin D levels. Yet, as the authors mentioned, trials of vitamin D supplementation seem to show no benefits for CVD. In addition, they state that benefits of high vitamin D levels for CVD might be a marker for something else. That something, of course, is probably sunlight. In their research, carried out by questionnaire, 23,593 women answered questions regarding melanoma. In addition, they also related factors of possible interest for hypertension. Those factors included detailed sun exposure habits, marital status, education, smoking, alcohol, BMI, exercise and chronic stress. Hypertension-medication use from 2005-2007 became the measurement tool used to determine hypertension incidence among members of the study group.
All subjects filled out a questionnaire to determine sun-exposure and sun-bed habits:
- Do you sunbathe during summer?
- Do you sunbathe during winter vacation?
- Do you travel south to sunbathe?
- Do you use a sun bed?
The investigators deemed that women answering ‘yes’ on one or two questions had moderate sun exposure. Those answering ‘yes’ on three or four questions had the greatest sun exposure.”
The main goal was to assess hypertension risk associated with sun exposure, after adjusting the data for any confounding factors.
Here are the results:
- When compared with women with high sun exposure, those with low sun exposure were 41% were more likely to have hypertension. For moderate sun exposure, the women were 15% more likely to have hypertension. Hence, this is another example of a dose response relationship (DRR). The lower the sunlight exposure, the greater the risk of hypertension.
- Other risk factors for hypertension were lack of exercise, darker skin, chronic high stress and lack of university education.
- The researchers concluded, “That in our observational design sun exposure was associated with a dose-dependent reduced risk of hypertension…. [This] might partly explain the fewer deaths of [from] cardiovascular disease with increasing sun exposure.”
Hypertension is serious, and a major cause of death, which is inversely associated to sun exposure. Therefore, regular, non-burning sun exposure can provide one of the best protections against this insidious disease.
For more information on sunlight and health: https://sunlightinstitute.org/ and read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Sunlight and food allergies are negatively associated. By Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Do certain foods cause you to break out in hives, or cause pain and discomfort? Then you may have an allergy and thus a hypersensitivity to the food. An allergy is a damaging immune response to a particular substance, to which the body is hypersensitive. In addition, in the case of anaphylaxis, it can be deadly. Sunlight and food allergies relate closely to each other, that is, in a good way. Hence, sunlight may have a place in stopping the allergic reactions.
A review of research on vitamin D, sunlight and food allergies makes some interesting statements. [1] First of all, the researchers state that since 2007, most epidemiologic studies have supported low sunlight, as a risk factor for food allergy. They then note that studies that looked directly at vitamin D status as measured by serum vitamin D levels are not nearly as consistent as studies on sunlight and food allergies. They state: “Although conflicting, the vitamin D studies suggest a more complicated association than a linear dose response in all individuals…”
However, sunlight exposure produces a different outcome for allergies.
Their summary is telling: “Many studies have linked sunlight with the development of food allergy. “However, whether this [directly relates] to vitamin D status or other sunlight-derived, seasonal and/or geographic factors remains uncertain. More studies are needed to investigate the role of sunlight and vitamin D status in food allergy because of their potential for primary prevention and disease modification.” Sunlight and food allergies may have a negative association. If more sunlight is available, fewer food allergies may occur.
This is another of those scientific papers that illustrates that sunlight exposure is nearly always protective against the studied disease. Yet, there is much more room for argument when vitamin D serum levels are used.
It is sunlight, not vitamin D, which makes the difference.
My takeaway? Sunlight and food allergies, since they are negatively related, speak to the importance of obtaining sufficient time in the sun. Get sufficient exposure to non-burning sunlight on a regular basis. That will provide plenty of vitamin D when one needs it. In addition, it also provides nitric oxide, endorphins, serotonin, dopamine, BDNF and other photoproducts yet unnamed. Thus, we must cease to equate sunlight exposure only with vitamin D. If vitamin D is our goal, and we neglect sunlight, we do a disservice to other healthful effects of sunlight. Furthermore, we must understand that a pill can never replicate the magnificent and essential powers of the sun.
Be sure to obtain your share of non-burning healing sunlight. For more information on the healing powers of sunlight, visit https://sunlightinstitute.org/. In addition, read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Sunlight and pandemics-more interesting information about our magnificent Sun, by Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Sunlight and pandemics link together closely—more sunlight, fewer pandemics. This is because it is our “best disinfectant.” Unobstructed sunlight kills viruses and bacteria outside the body and strengthens the body internally. Sunlight has been preventing diseases throughout history. That is probably why the sun was a deity in some ancient societies. More recently, scientists have been telling us for decades how important sun exposure is, and they continue to do so.
Perhaps it is time to listen!
Thus, research early in 2020, from the DHS, showed that “simulated sunlight” rapidly decayed the Covid-19 virus. The researchers tested effects of sunlight on Covid-19 viruses in aerosols—suspensions of solid particles and liquid droplets in air. These aerosols are a potential route of disease transmission through inhalation. Consequently, when sunlight exposure accelerates the decay of these viruses, it prevents an avenue of human-to-human transmission. Thus, the breathing in of these “decayed” viruses, usually coughed, sneezed, or exhaled, ceases to be lethal. Therefore, sunlight outside the body inactivates the viruses due to rapid decay. In other words, it kills them before they can do damage.
Sunlight and pandemics also link internally through vitamin D production.
Vitamin D, produced by skin during sun exposure, also inhibits some of the powerful disease reactions and makes pandemics less deadly. The cytokine storm is one of those reactions. It may lead to death by causing inflammation and subsequent pneumonia. A cytokine is a specialized protein molecule that attacks and destroys infected tissue. These proteins can be either pro-inflammatory of anti-inflammatory. For our purposes, we will discuss pro-inflammatory cytokines.
How does the cytokine storm work?
Usually, the cytokines needed to fight the infected tissue, cease their attacks and diminish after they have won the battle. However, in the case of a disease like influenza (or Covid-19), “friendly fire” occurs. The immune system recruits millions of reinforcing cytokines, and those cytokines mount an overwhelming attack against tissue they initially protected. In other words, they cause a violent storm. Cytokine storms lead to severe inflammation that weakens or destroys blood vessel membranes in the lungs and other tissue. As a result, fluid seeps through to the air sacs, which leads to pneumonia. People thus end up drowning in their own body fluids. Dr. Angela Rasmussen describes it: “Basically you’re bleeding out of your blood vessels.” She goes on to say the problem may not end there. The storm spills into the circulatory system and can create systemic issues across multiple organs.
How does vitamin D dampen the storm?
Vitamin D leads to the production of cathelicidins and defensins, which are peptides (proteins) with antimicrobial properties. According to Dr. William Grant and colleagues, these peptides lower viral replication rates and reduce concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines. As already mentioned, these pro-inflammatory cytokines produce the inflammation that injures the lungs. Nevertheless, the damage does not necessarily end in the lungs. Recent research shows that the damage from Covid-19 can spread to multiple organ systems.. The report on this research suggests the cytokine storm may be responsible for that spread. The heart, liver, kidneys, neurological system and gastrointestinal tract may all be targets of Covid-19.
If what I posit is true, we would expect Covid-19 to be higher in populations with high vitamin D deficiency, and such is the case.
Henry Lahore, one of the great vitamin D scholars, has listed four racial groups with disproportionately high vitamin D deficiency: Elderly Italians, Spanish, Swedish Somalis and African Americans. Mr. Lahore furnishes invaluable information regarding race, vitamin D, sunlight and Covid. Many of you have read of the alarmingly high Covid-19 death rate in African Americans. From my previous research, I know that African Americans also have alarmingly low vitamin D levels. Lahore also cites research that shows 84% of African Americans are vitamin D deficient. In addition, in Chicago, 70% of Covid 19 deaths are among Blacks. The reason for the deficiency? Dark skins take much more time in the sun to produce vitamin D.
Unfortunately, our answer to Covid-19 has been to cocoon everyone indoors.
The lockdowns assure that no one can obtain vitamin D except by supplement. That is, unless they are fortunate enough to own sunlamps and sunbeds (tanning beds). Even more alarming is the fact that the Swedish Somali population has 40% of the deaths in Sweden. Yet, they comprise only .84% of the Swedish population. Therefore, the Dark-skinned Somalis have 4,700% greater risk of death from Covid 19! This can only be due to lack of sufficient sunlight and subsequently, low vitamin D. No such death risk exists in Africa, where sunlight is ubiquitous. Thus, the answer for all Americans is to obtain plenty of non-burning sun exposure year around, or use a sunbed.
More common sense about sunlight and pandemics from Richard Hobday, researcher and writer.
First of all, to understand this section, you must know that the flu pandemic of 1918 killed approximately 50 million people. Mr. Hobday explains this in an important paper from 2020, entitled Coronavirus and the Sun: a Lesson from the 1918 Influenza Pandemic
Here are his most impactful points regarding sunlight and the 1918 pandemic:
Medical personnel found that patients nursed outdoors recovered better than those treated indoors.
- Outdoor air is a natural disinfectant. Fresh air can kill flu viruses and other germs.
- In the 1918 pandemic, overcrowding and bad ventilation put soldiers and sailors at high risk of catching influenza.
- Most of the victims of the pandemic did not die from influenza: they died of pneumonia and other complications.
- Hospital personnel placed sick soldiers outdoors to breathe fresh air [and of course, sunlight]
- Open-air treatment reduced deaths among hospital patients from 40 percent down to about 13 per cent.
Of course, in 1918, the efficacy of sun exposure and vitamin D was unknown.
So now, we know. Low sunlight links to high pandemic risks. More sunlight and fresh air produce a better chance of surviving the pandemic we currently face.
It seems like nature knew a better way more than 100 years ago. Safely enjoy non-burning sun exposure or sunbed exposure regularly.
Happy Sunning!
To learn more about the marvelous curative powers of sunlight, visit Sunlight Institute and read the Book, Embrace the Sun.
MS is associated closely with lack of sun exposure and low vitamin D levels. So what is new? By Marc Sorenson, EdD
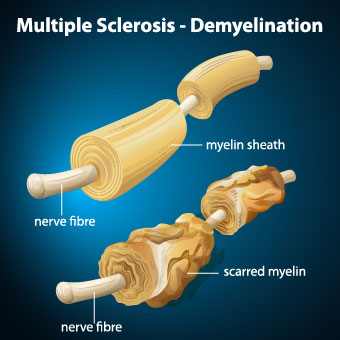
MS is a disabling autoimmune disease.
MS is an autoimmune disease in which T-cells initiate an inflammatory response against myelin. This process, known as demyelination, leaves the nerves bare and susceptible to “short circuiting.” As a result, communications between brain and body suffer damage. Eventually, the disease causes irreparable deterioration of nerves. Some of the effects of MS include numbness and weakness in limbs. In addition, there may be lack of coordination, loss of vision, lack of mobility, slurred speech and numerous other disorders.
What do we know about the connection between sun exposure and MS?
Sunlight is an immunomodulator. In other words, it may affect the functions of the immune system. In the case of an autoimmune disease, it may stop the immune system’s attack on its own tissue. Because sunlight stimulates the production of vitamin D in skin, it may suggest that vitamin D is protective. In addition, it also suggests the incidence should diminish in areas of high sun exposure, and increases in areas of low exposure.
Thus, the risk of MS in far northern areas is 100 times greater than in equatorial areas.
In equatorial areas, sunlight is intense, and the risk of the disease approaches zero. Another interesting study of immigrants to the UK (low sunlight), but born in the sunny West Indies is enlightening. Especially relevant is that these immigrants had one-eighth the rate of MS as their own children born in the UK. It therefore appears that childhood sun exposure provides protection against the disease.
Where does vitamin D fit?
While it is tempting to chalk up the association of low MS to high vitamin D (as mentioned above), use caution. As with certain other diseases, sun exposure may have a positive influence on MS, independent of vitamin D. For example, a study on animals assessed the relative affect of sunlight and vitamin D on the diseaase. The researchers concluded, “These results suggest UVR [sun] is likely suppressing disease independent of vitamin D production.” They also stated that vitamin D supplementation alone might not replace the ability of sun (UV) to reduce MS susceptibility.
Another more recent study found similar results.
The investigators used animals that had no vitamin D receptors (VDR), and therefore could not produce vitamin D. Therapy with UV light suppressed the disease. The investigators concluded that UV light suppression of MS occurs in the absence of vitamin D production.
Another recent investigation: High sun exposure and high vitamin D both associate with lessened severity of MS.
This study investigated the severity of the disease among people who already had MS. Thus, it was a unique study, to my knowledge. The investigators used the subjects’ latitude (a marker for sun exposure and vitamin D levels) and compared it to MS severity. Interestingly, high sun exposure and high vitamin D levels associated to a reduction in MS severity. However, the investigators listed only sunlight as a sure factor in reducing MS severity.
Hence, the investigators stated three salient points in their paper.
- “Observational studies suggested vitamin D-dependent effects, but prospective supplementation studies have so far been inconclusive….”
[This is an important, and a wake up call. Those who believe that we need only swallow a handful of pills, as we avoid the sun, are sadly mistaken. There is no way we can determine if high vitamin D blood levels are the reason for a reduction in MS severity. That is, unless we produce those levels in a scientific, controlled study using supplementation.]
- “Although [low] vitamin D cannot be proven as the causal factor, we provide evidence for clinically relevant effects of sunlight exposure.
- ”Furthermore, this study suggests sunlight triggered pathways other than vitamin D could play additional and modulatory roles as well.”
There you have it.
High sunlight exposure decreases the severity of multiple sclerosis. Vitamin D, though it is a miraculous nutrient, probably has little or no effect on the disease.
HAPPY SUNNING!
 You can find much more information on sun exposure and MS at sunlightinstitute.org. Also, read the book, Embrace the Sun.
You can find much more information on sun exposure and MS at sunlightinstitute.org. Also, read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Fishermen receive skin protection through sun exposure and vitamin D, by Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Fishermen in Brazil spend plenty of time on the sea and have healthy skin. Furthermore, they soak up vast quantities of direct sun exposure. Thus, should we expect them to succumb to incredibly high rates of skin cancer? No! Does this seem like a paradox? It should not. It is the perfectly natural outcome of plenty of non-burning sun exposure. This will seem clear to you if you have read my book, Embrace the Sun.
Recent research from Brazil produced some large and fascinating surprises. In addition, it changed a few minds regarding knowledge of sunlight’s healthful qualities. First of all, it illuminated sunlight’s protective effects against skin cancer, particularly in fishermen.
So how much sunlight do fishermen in Brazil soak up daily?
Due to their profession, commercial fishermen chronically expose themselves to sunlight. So, in this research, they had soaked up Brazilian sunlight for more than 15 years. The average exposure time was 21 to 28 hours weekly! Consequently, these fishermen received a sunlight dose 6-8 times higher than indoor workers did. Therefore, you might surmise that they used lots of sunscreen. Yet they did not. It is especially relevant that 62% of this population of fishermen used none. Must we therefore conclude that they suffered exceptionally high skin cancer risk? No. The frequency of skin-cancer diagnoses was 2.7% of the study population of 174 fishermen (and fisher women). The researchers stated, “There was a low prevalence of diagnosed skin cancer among the fishermen when compared to the general population.”
So there you have it. The general population, with comparatively little sun exposure, suffers from a high skin cancer risk.
Yet, fishermen practically bake in the sun every day, and have a minuscule risk of skin cancer. This paradox should be easily understood. Sun exposure is a superb prophylactic against skin cancer and most other cancers if used regularly and safely without burning. Remember that it causes the body to produce vitamin D, which may also provide protection against skin cancer.
For more information on sunlight and health, visit sunlightinstitute.org and read the book, Embrace the Sun.
HAPPY SUNNING!
More sunlight, less covid 19 by Marc Sorenson, EdD.
More sunlight, I said at the onset of Covid-19 (also known as SARS-Cov-2), would be associated with a reduced incidence disease and death. In addition, I stated the disease would make a remarkable resurgence in fall and winter, as availability of sunlight diminished. For that statement, some praised my perspicacity, and others derided my intelligence. I lost some friends on social media and had to unfriend others.
For our purposes, it is important to understand that there are several coronaviruses, and each causes its particular disease manifestation.
In addition, with the possible exception of Covid-19, these viruses are seasonal. Thus, the incidence rates are higher in winter and lower in summer. Could sunlight exposure be the key to the seasonal relationship? Especially relevant, of course, is that Covid-19 was non-existent at the time the other viruses proved their seasonality. It now appears, however, that Covid-19 is indeed seasonal. Thus, I believe that sunlight drives that seasonality.
So what do we to obtain more sunlight now that winter has arrived?
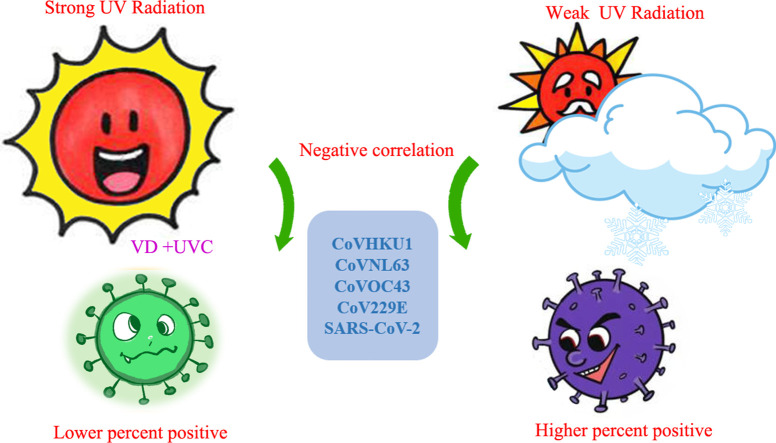
I suppose it is self-serving to say, “I told you so.” Yet indeed, I did make my prediction, and it was correct. It would have been even more correct if people were encouraged to seek the sun rather than suffer through sunless lockdowns. There is now scientific corroboration that more sunlight associates with less death and disease from Covid-19 and other coronaviruses. Recent research (already dated for 2021), substantiates my ideas on sunlight and Covid-19. In this study, the investigators assessed sunlight available from April 17-July 20, 2020 in various U.S. geographical zones. Then, they compared sunlight availability to the risk of Covid-19 and four other coronaviruses in different areas of the U.S. The graphical abstract they presented is below and makes the same point that I made months ago.
In areas of strong UV radiation (more sunlight), there was much less risk of testing positive for Covid-19 and the other coronaviruses.
Obviously, people need more sunlight to help protect themselves from Covid-19 and other viruses. Obtaining more sunlight works in at least two ways against Covid-19.
1. Research from the CDC shows that sunlight rapidly kills Covid-19 in aerosols.
Aerosols are suspensions of solid particles or liquid droplets in air. They are potential routes for disease transmission. Sunlight is also able to kill Covid-19 on surfaces.
2. More sunlight exposure causes the skin to produce more vitamin D
. Vitamin D inhibits the overproduction of cytokines, specialized protein molecules that attack and destroy infections. Usually, the cytokine needed to fight the infected tissue stops its attack after it has won the battle. However, in the case of a disease like influenza (or Covid-19), “friendly fire” occurs. The body’s immune system recruits innumerable “extra” or reinforcing cytokines, and those cytokines mount an overwhelming attack against the tissue they initially protected; in other words, they cause a cytokine storm.
Cytokine storms lead to severe inflammation that weakens or destroys blood vessel membranes in the lungs.
This causes fluid to seep through to the air sacs, which leads to pneumonia. A person then ends up drowning in his/her own body fluids. Dr. Angela Rasmussen describes it thus: “Basically you’re bleeding out of your blood vessels.” She goes on to say that the problem may not end there. The storm spills into the circulatory system and can create systemic issues across multiple organs.
Vitamin D, through various mechanisms, retards and stops cytokine storms.
Thus, sun exposure is a two-edged sword: (1) it kills Covid-19 outside the body. (2) It causes the production of vitamin D and can stop the cytokine storm.
So in winter, when there is little sunlight available, and virtually no production of vitamin D, what shall we do?
When there is insufficient sunlight, it is essential to find another source of light that will also produce vitamin D. Sunbeds are the ideal source of the light we seek. Research shows that sunbed users (tanning bed users) in Canada and the U.S. have higher vitamin D levels than any other demographic.
I own a sunbed and go to salons when traveling. This winter, I plan to use my sunbed regularly. In my opinion, it is the best protection against the sunlight deficiency experienced in winter.
For more information on the healthful benefits of sunlight, visit https://sunlightinstitute.org/ and read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Happy sunning!
IQ, vitamin D and sunlight by Marc Sorenson, Ed.D
IQ and vitamin D levels piqued my interest many years ago. This was because research had demonstrated that animals with low vitamin D levels had poorer neurocognitive function. For example, rats born to vitamin D-deficient mothers have profoundly altered brains at birth. The cortex is longer, the lateral ventricles enlarged the cortex thinner, and there is more cell proliferation. Furthermore, there are also reductions in brain content of nerve growth factor. In addition, similar results manifested themselves with older rats born to vitamin D-deficient mothers.
Other research indicates IQ, vitamin D and sunlight have a connection to cognitive function:
Here are more reasons to believe brain and cognitive function associate closely with IQ, as well as vitamin D and sunlight. The book Embrace the Sun. covers the following facts thoroughly:
- Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and non-Alzheimer’s dementia associate with low vitamin D levels and insufficient sun exposure.
- Autism associates with low vitamin D levels. Bipolar disorder associates with both sun exposure and low vitamin D levels.
- In addition, a study of cognitive abilities as they relate to vitamin D levels shows a considerable difference in vitamin D deficient people. Thus, persons with lowest levels are twice as likely cognitively impaired compared to those with highest levels. Remember that sun exposure raises and optimizes vitamin D levels.
- Another study showed twice as many patients with intellectual disabilities showed D deficiency when compared to normal controls.
Back to IQ
Despite the aforementioned facts and research, I had never seen research that associated IQ in humans to sunlight. Consequently, I searched the literature for years, and have now found my research. A most interesting article on IQ, vitamin D and sunlight recently appeared in the Journal of Nutrition. In this study, the researchers assessed pregnant women for vitamin D levels and then assessed their subsequent offspring for IQ.
The researchers assessed these women’s vitamin D levels in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Offspring of women with low vitamin D levels had lower IQs at the age of 4-6 years. The researchers concluded thusly: “Second-trimester maternal vitamin D positively associated with IQ at 4–6 y, suggesting that gestational vitamin D status may be an important predictor of neurocognitive development. These findings may help inform prenatal nutrition recommendations and may be especially relevant for Black and other dark-skinned women at high risk of vitamin D deficiency.
The bottom line regarding IQ.
Pregnant mothers need to optimize their vitamin D levels, preferably by sun exposure to the skin. It will ensure that both they and their offspring will be healthier and smarter. This is vitally important to black women and other women of color, who have large quantities of skin melanin. This inhibits vitamin D production and may be dangerous for their offspring. IQ, vitamin D and sunlight are important to well-being and happiness. Nevertheless, the researchers observed no IQ differences based on race, but only on vitamin D Levels.
For more information on the health benefits of sunlight and vitamin D, visit Sunlight Institute and read the book, Embrace the Sun. 
Happy sunning!
Mental illness: Vitamin D deficiency, and thereby sunlight deficiency, plays a major role. By Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Mental illness is a pandemic in the United States. Nearly one in five U.S. adults live with a mental illness (46.6 million in 2017). Mental illness has multiple causes and manifestations. It is especially relevant to understand that sunlight deprivation, leading to vitamin D deficiency, plays a major role in this disorder. It is also important to realize that sun exposure, for typical people, produces about 90% of serum (blood) vitamin D. In addition, this production occurs when midday sunlight touches the skin. However, vitamin D is only one of several photoproducts produced by sun exposure to skin or other body parts. In addition, sun exposure produces serotonin, endorphin, dopamine, and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). Furthermore, all of these vital chemicals has a profound influence on mental Illness.
An important study on vitamin D
The disease is ubiquitous, as is sun deprivation. Thus, thus an investigation on vitamin D and mental illness reminded me of the affects of sunlight. This laboratory-based study found a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among 290 patients with mental illness. Consequently, Only 18% of these patients showed adequate levels of vitamin D. To me, this also means that only 18% were obtaining sufficient sun exposure for good mental health and well-being. The researchers concluded that sensible sun exposure could be a boon to mental health.
Let us now discuss a few of the disorders classified as types of mental illness. Then we will also mention the research that indicates an impressive salutary influence of sun exposure.
ADHD, a mental illness of children
ADHD ( attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is the most prevalent of all mental disorders in children. Hence, it causes significant problems with executive functions, leading to hyperactivity or impulsiveness not appropriate for the person’s age.
Researchers have found that sun exposure correlates to a decreased risk of ADHD. They assessed the relationship between the prevalence of ADHD and the intensity of the sun in various nations and in US states. And after adjusting for birth weights, infant mortality and other relevant factors, the findings were not altered. It was obvious that sun deprivation by itself was associated with a higher risk of ADHD.
Autism, another disease of youth
Is autism a sun-deficiency disorder? Autism rates are increasing exponentially and associate to vitamin D deficiency, which, of course, associates to sun deficiency. The Autism Society of America defines autism as “a complex developmental disability typically appearing during the first three years of life and is the result of a neurological disorder affecting the normal functioning of the brain, impacting development in the areas of social interaction and communication skills. Both children and adults with autism typically show difficulties in verbal and non-verbal communication, social interactions, and leisure or play activities.”
If vitamin D deficiency and/or sun deprivation relates to autism, symptoms should improve in summer. Thus, a case study reported by Dr. Cannell revealed improvements in autism-related sleep and behavioral problems during summer. Autistic traits such as crying, excitability, hyperactivity and pounding objects profoundly diminished during summer.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder (BPD), also known as manic-depressive illness, is a brain disorder causing unusual shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, and the ability to perform day-to-day tasks. Symptoms are severe and can result in damaged relationships, poor job or school performance and even suicide.https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/bipolar-disorder/index.shtm
Sun exposure resets the body’s circadian rhythms, which are variations in physiology and behavior persistent with a cycle length close to 24 hours. This system is contained in the hypothalamus and stimulated by nerve cells in the retina of the eye in response to light. Research indicates that environmental conditions early in life may imprint the circadian system and influence mental function later in life: Increased number of hours of daylight at the location of birth during the first three months of life are associated with a significantly older age of onset of bipolar disorder. For a longer discussion on bipolar disorder, read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Cognitive disabilities (intellectual disorders)
Another research study, based on a 15-year residential history of varying degrees of sun exposure, produced an interesting result. It showed that cognitive impairment in persons who were below the median exposure to sunlight was 88% greater than in those who were above the median. These same investigators had previously shown that lower levels of sun exposure resulted in a 2.6-times higher incidence of cognitive impairment. Therefore, if you want to think clearly and keep your marbles, regularly soak up some non-burning sunlight.
Depression
Few people realize how prevalent depression is in our society, a mental illness representing a huge drain on the economy. Moreover, according to Steven Genuis, in an editorial in Canadian Family Physician, “The World Health Organization estimates depression costs the American economy about $44 billion annually, equal to the total cost of all cardiovascular diseases.” He also stated that in one decade, there was a 300% increase in the sales of antidepressants, making these medications the top-selling pharmaceuticals in the world. (Genuis, S. Keeping your sunny side up (editorial). Canadian Family Physician 2006:52:42-43.)
So what does the sun do to relieve “the blues?”
The answer probably lies in a chemical responsible for transmitting impulses between nerve cells. This “neurotransmitter,” serotonin, is a natural “upper,” and works in synchronization with the natural “downer,” melatonin. When we awake to sunshine, light enters the eye and stimulates serotonin production. We then quickly become awake and invigorated, and melatonin diminishes. Nevertheless, at day’s end, the bright light disappears (or at least it should), melatonin levels rise, and serotonin levels diminish. We begin to feel sleepy and ideally retire for a good night’s rest. It is a perfect system for our needs—unless we stay up beyond biologically natural hours, by using artificial lighting. Many experts believe that lack of serotonin is a cause of depression.
The most important study on serotonin
Though I mentioned this study in my previous blog on sunlight and depression, it bears repeating here. Dr. Gavin Lambert performed one of the most important and unique studies on serotonin. He and his colleagues measured serotonin levels in response to varying degrees of sunlight. First of all, they drew blood samples from the internal jugular veins of 101 men. In addition, they compared the serotonin concentrations of the blood to weather conditions and seasons. As a result, men measured on a bright day produced eight times more serotonin, than those measured on a dismal day. Of course, the mood improved due to sunlight, with no involvement whatsoever of vitamin D. Thus, regular, non-burning sun exposure is the answer to depression. In addition, remember that sun exposure also leads to the production of other mood enhancers such as nitric oxide, endorphin and dopamine.
Certainly, sunlight deprivation is not the only cause of mental illness, but it is one of the most important.
There are more mental illnesses to discuss, and I will expatiate on those in a future article. In the meantime, protect your mental health by being sure to obtain your share of non-burning sunlight. For more information, visit sunlightinstitute.org, and read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Depression, vitamin D and sunlight. Which is more important? By Marc Sorenson, EdD
Depression is a national horror made worse by fear, worry and lack of sunlight. The Covid-19 pandemic and the tendency to lock people away from sunlight and fresh air has taken an enormous toll.
Depression is more likely to respond to sunlight and vitamin D than sedentary living. That is the message I derived from a recent study. First, the purpose of the research was to estimate cumulative vitamin D doses in 96 depressed patients. These vitamin D doses came from two different sources: solar ultraviolet light, and dietary intake. Another part of the research was to compare vitamin D doses of these depressed patients to 96 age- and sex-matched healthy (non-depressed) controls.
Here are the “Enlightening” results and conclusions.
According to the researchers, there was the major (and probably unexpected) finding. Those with depression had significantly lower vitamin D doses compared to age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Thus, the research again proves the efficacy of sunlight (and possibly vitamin D) for reducing depression. Nevertheless, there was a more important conclusion as stated by the investigators. “While dietary intakes of vitamin D were equal in both groups, patients with depression appeared to have statistically significantly less vitamin D from solar ultraviolet B.” This statement is of transcendent importance due to the establishment of an important fact. That fact is that a superior form of vitamin D results from sun exposure.
Other points to remember regarding sunlight and depression.
In addition to this study, numerous other investigations corroborate the efficacy of sun exposure for ameliorating depression. Serotonin is a potent “upper” that improves mood almost immediately. Sunlight produces Serotonin when it enters the eyes.
The most impressive study on serotonin, sunlight and depression.
Dr. Gavin Lambert did one of the most important studies on serotonin. He and his colleagues measured serotonin levels in response to varying degrees of sunlight. To do so, they drew blood samples from the internal jugular veins of 101 men and compared the serotonin concentrations of the blood to weather conditions and seasons. The remarkable results: Men measured on a bright day produced eight times more serotonin, compared to those measured on a dismal day. Of course, the mood improved due to sunlight, with no involvement whatsoever of vitamin D. Thus, regular, non-burning sun exposure is the answer to depression. In addition, remember that sun exposure also leads to the production of other mood enhancers such as nitric oxide, endorphin and dopamine.
For more information regarding sunlight and depression, visit sunlightinstitute.org and read the book, Embrace the Sun.
Happy sunning!