Melanoma risk between persons with high and low vitamin D levels
Melanoma Risk By Marc Sorenson, EdD, Sunlight Institute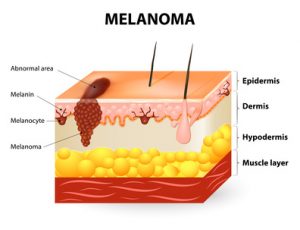
The risk directly associates with low levels of vitamin D. That is the conclusion of recent study published in the European Journal of Cancer.[1] The investigators measured the blood vitamin D levels of 137 subjects who had been diagnosed with melanoma. They collected the blood samples at the time of diagnosis of the disease. Another group of 99 healthy subjects served as the control group. The investigators collected the samples of the control group between October and April. The scientists then compared the blood collections of the melanoma group with those of the control group. They then determined whether vitamin D levels had an association with melanoma risk.
The study produced convincing results regarding vitamin D and melanoma risk.
The results were as follows:
- The controls (no melanoma) had vitamin D levels 50% higher than the melanoma group (27.8 ng/ml vs. 18 ng/ml).
- 66.2% of the melanoma group had vitamin D “deficiency,” compared to only 15.2% of the health controls. The scientists defined vitamin D deficiency as being equal to or less than 20 ng/ml. So, the melanoma group had more than four-times the risk of deficiency.
- The scientists defined vitamin D “sufficiency” as being equal to or greater than 30 ng/ml. They found that only 7.4% of melanoma patients were sufficient, compared to 37.4% of healthy controls. Hence, the melanoma group had about one-fifth the likelihood of having sufficient D levels.
More scientific analysis on vitamin D measurements vs. melanoma risk
The scientists then adjusted the data for possible confounding factors such as age, sex and body mass. Then, they performed an analysis that showed the following:
- First of all, the science demonstrated a significant inverse association with vitamin D sufficiency versus deficiency. Those who had sufficient levels had only 4% of the melanoma risk when compared to those who were deficient! Hence, this demonstrates that those with the lowest vitamin D levels (after adjusting for confounding factors) had 25-times the melanoma risk!
- And, vitamin D insufficiency vs. deficiency was significantly inversely associated with melanoma. Those who were insufficient had a definite advantage over those who were deficient. They had only 13% of the melanoma risk.
Now, this is the most important point about melanoma risk:
In addition, this research proves conclusively that sun deprivation is a major cause of melanoma. I say this because about 90% of serum vitamin D is produced by sun exposure to the skin.[2] So, the aforementioned research is really research on sun exposure. It shows that regular sun exposure leads to a profound reduction in melanoma risk. Therefore, Vitamin D levels are surrogate measurements for sun exposure in nearly every case.
Could sunlight increase health through photoproducts beyond vitamin D?
In conclusion: My new book, Embrace the Sun (coauthored by Dr. William Grant), notes that sun exposure provides more than vitamin D. It also provides other photoproducts such as nitric oxide, serotonin, endorphin, and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). All of these photoproducts are vital to human health. Could these photoproducts have a positive and protective effect against melanoma risk beyond vitamin D? And, vitamin D produced by sunlight may be superior to that given in pill form.
Finally, this research gives us one more reason to embrace the sun safely without burning. And who would have thought that safe sunlight could be one of the best prophylactics against melanoma risk?
Happy sunning!
The book is available at Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/Embrace-Sun-Marc-B-Sorenson/dp/069207600X/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid=1533923845&sr=8-1&keywords=embrace+the+sun+sorenson
1] Cattaruzza MS, Pisani D, Fidanza L, Gandini S, Marmo G, Narcisi A, Bartolazzi A, Carlesimo M. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D serum levels and melanoma risk: a case-control study and evidence synthesis of clinical epidemiological studies. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2018 Feb 12. [Epub ahead of print]
[2] Reichrath J. The challenge resulting from positive and negative effects of sun: how much solar UV exposure is appropriate to balance between risks of vitamin D deficiency and skin cancer? Prog Biophys Mol Biol 2006;92(1):9-16
Breast cancer breakthrough.  By Marc Sorenson, EdD. Sunlight Institute
By Marc Sorenson, EdD. Sunlight Institute
Stunning Breast Cancer research shows that the highest vitamin D levels associate with an 80% reduction in risk.[1]
Is the breast cancer pandemic due to vitamin D deficiency?
First of all, as pointed out by the authors, numerous studies have shown an association between higher vitamin D level and breast cancer. But, other studies had not taken into consideration serum levels of vitamin D above 40 ng/ml. Why? Because that level had been considered the highest level needed for good health. Nevertheless, this study showed differences in breast cancer risk when comparing all serum vitamin D levels, and that made all the difference in the results. The research included 5,038 women .
.
A dose-response association between vitamin D levels and breast cancer
The most noteworthy finding can be summed up in the study conclusions: “Higher 25(OH)D concentrations were associated with a dose-response decrease in breast cancer risk with concentrations ≥60 ng/ml being most protective.” In other words, the higher the vitamin D levels, the greater was the protection.
This fact is especially relevant: serum vitamin D levels in 90% of the population are effected by sun exposure. Hence, sun exposure may be the operative factor in the comparisons. Sun exposure causes the body to produce nitric oxide, serotonin, endorphin and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). Most noteworthy is that all of these photoproducts are vital to human health.
Is something besides vitamin D at work in preventing breast cancer?
Therefore, it could be that these additional photoproducts added power to the vitamin D produced by the sun. Could the “holistic” sun be more important than vitamin D alone? Of course it is! Another study, little known, may hold the answer. An investigation from Iran, on the association between breast-cancer risk and vitamin D, showed that low vitamin D predicted only a slightly increased risk of the cancer. However, among women who totally covered themselves and thereby had no sun exposure, there was a 10-fold increase in the risk of the disease.[2] In other words, there was a 1,000% increase in breast cancer risk due to sun deficiency.
Summary:
Finally, consider this: With the holistic sun, we get the entire package, not just vitamin D. Embrace the Sun, and don’t burn.
For more on the study, see the press release put out by the Vitamin D Society: http://www.vitamindsociety.org/press_release.php?id=58
[1] Sharon L. McDonnell , Carole A. Baggerly, Christine B. French, Leo L. Baggerly, Cedric F. Garland, Edward D. Gorham, Bruce W. Hollis, Donald L. Trump, Joan M. Lappe. Breast cancer risk markedly lower with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations ≥60 vs <20 ng/ml (150 vs 50 nmol/L): Pooled analysis of two randomized trials and a prospective cohort. PLoS One. 2018 Jun 15;13(6)
[2] Bidgoli SA, Azarshab H. Role of vitamin D deficiency and lack of sun exposure in the incidence of premenopausal breast cancer: a case control study in Sabzevar, Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(8):3391-6.
MS prevention by sunlight. By Marc Sorenson, Ed.D. Sunlight Institute
What is MS?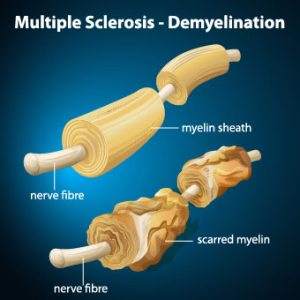
MS is a painful, debilitating, crippling, disease in which immune cells initiate an inflammatory response against myelin. Myelin is the nerves’ protective cover. It is rather like an electric wire that has lost its rubber cover. So, this process, known as demyelination, leaves the nerves bare and susceptible to “short circuiting.” From 85 to 170 people per 100,000 in the USA suffer from MS, and the rate among women, during the period from 1991 through 1994, has increased by 50% compared to the period from 1982 through 1986. Also, as of 2010, the last year for which we could find statistics, there were 350,000-400,000 cases diagnosed in the USA.
There is no doubt that sunshine reduces the risk of MS, because The risk of multiple sclerosis in far northern areas, where there is little sunshine, is more than 100 times greater than it is in equatorial areas. So, in those areas, where sunlight is intense, due to directness of the sun, the rate of MS approaches zero. [1], [2], [3]
And do you know anyone who suffers from multiple sclerosis? They should probably read this blog and then obtain plenty of non-burning sun exposure.
The latest Research on MS, sun exposure and vitamin D.
A study carried out in Southern California corroborates the sun exposure benefits to MS reduction.[4] First of all, the researchers recruited members of three different ethnicities (blacks, Hispanics and whites). In addition, they further divided those ethnicities into those who suffered from MS (known as cases) and those who were free from the disease (controls). They then simultaneously examined lifetime sun exposure and blood vitamin D levels, accounting for genetic ancestry and other factors. The results were impressive:
- Among blacks, the highest lifetime sun exposure was associated with a 47% lower risk, independently of blood levels of vitamin D.
- Among whites, the highest lifetime sun exposure was associated with a 32% lower risk. In this group, highest vitamin D levels also associated with a lower risk of MS.
- Among Hispanics, the highest lifetime sun exposure was associated with a 34% lower risk, independently of blood levels of vitamin D.
This is just the latest research to determine that sun exposure lessened the risk of MS independently of vitamin D. In addition, researchers used animals with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) (an experimental form of MS). It was induced in animals in a lab setting and then used to determine the relative influences of UVR and vitamin D on MS. In conclusion, they stated, “These results suggest UVR [sun] is likely suppressing disease independent of vitamin D production. Thus, vitamin D supplementation alone may not replace the ability of sun (UV) to reduce MS susceptibility.”[5]
More on sunlight and MS from the same researchers
Later on, some of these same researchers investigated the mechanism by which sun exposure suppressed the disease and determined that UV light selectively inhibits spinal cord inflammation and demyelination.[6]
Furthermore, in another study, scientists performed an investigation with UVR. UVR is the same radiation emitted by the sun and sunbeds or sunlamps. It was administered to animals with EAE.[7] First of all, the researchers found that UVR treatments stopped inflammation and demyelination of the spinal cord. It did so by inhibiting a chemical known as a chemokine, also known as a cytokine. Cytokines are specialized proteins that are either inflammatory or anti-inflammatory in their nature. Therefore, inflammatory cytokines or chemokines are the cause of inflammation and autoimmune attacks resulting in MS. In addition, UVR directly initiated the MS-ameliorating effects, independent of vitamin D.
To conclude:
Finally, as wonderful as vitamin D is, we should realize this: The production of vitamin D is only one of the profoundly healthful effects that are due to Sun Exposure. Hence, those who take vitamin D and believe they will derive all the benefits of sun exposure, are wrong. Consequently, they could be “dead wrong” in the case of a scourge like MS. So, be sure to obtain your full share of non-burning sunlight whenever possible. It could save your life. And, it could save the lives of those who have the disorder or who might be susceptible to it. Maybe we should start paying more attention to our sun exposure?
This is one of many blogs that I and others have written on this subject. In addition, here are a few more that may interest you:
http://sunlightinstitute.org/research-shows-sun-exposure-thwarts-multiple-sclerosis-ms/
http://sunlightinstitute.org/a-vitally-important-study-on-sunlight-and-multiple-sclerosis-ms/
Embrace the sun! Without burning, of course
[1] Alter M, Yamoor M, Harshe M. Multiple sclerosis and nutrition. Arch Neurol l974;31:267-72.
[2] Kurtkze, J. Geography in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 1977;215:1-26.
[3] Hayes CE, Cantorna MT, DeLuca HF.Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1997;216:21-27
[4] Langer-Gould A, Lucas R, Xiang AH, Chen LH, Wu J, Gonzalez E, Haraszti S, Smith JB, Quach H, Barcellos LF. Nutrients. 2018 Feb 27;10(3).
[5] Becklund BR, Severson KS, Vang SV, DeLuca HF. UV radiation suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis independent of vitamin D production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:6418-23.
[6] Wang Y, Marling SJ, Beaver EF, Severson KS, Deluca HF. UV light selectively inhibits spinal cord inflammation and demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 1;567:75-82
[7] Wang Y, Marling SJ, Beaver EF, Severson KS, Deluca HF. UV light selectively inhibits spinal cord inflammation and demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 1;567:75-82.
Obesity: Do vitamin D and sunlight have a part? A new study shows that when vitamin D-deficient pregnant women bear children, the children may become obese.[1] Furthermore, the children had larger waistlines at age 6, compared with children born to women who had sufficient vitamin D levels. The body-fat percentage of those born to vitamin D- deficient women was also significantly higher. Body fat-percentage is a measure of obesity (or lack thereof).
when vitamin D-deficient pregnant women bear children, the children may become obese.[1] Furthermore, the children had larger waistlines at age 6, compared with children born to women who had sufficient vitamin D levels. The body-fat percentage of those born to vitamin D- deficient women was also significantly higher. Body fat-percentage is a measure of obesity (or lack thereof).
The authors stated that 95% of vitamin D production in the body comes from sun exposure to skin. That is correct. Consequently, the expectant mothers spend too much time indoors. Or, they are frightened into sunscreen use, which can prevent production of 99% of vitamin D by sun exposure. Therefore, this type of obesity is a sun-deprivation disease. The research suggested that vitamin D supplements might be the answer. However, the answer is not supplements when sunlight is available. We should promote safe, non-burning sun exposure to prevent obesity.
Much has been researched lately regarding the importance of sunlight in preventing obesity. In my last blog, I mentioned several of these studies: http://sunlightinstitute.org/staying-slim-sunlight/
Here is a list of the methods by which sun exposure helps to prevent or reverse obesity:
- First of all, because blue-spectrum light causes cells to dump part of their fat load, it helps weight-control
- Secondly, early-morning light, because it resets circadian rhythms, reduces the risk of weight-gain.
- Thirdly, exposure to ultraviolet radiation (one of the spectrums in sun exposure) has been shown to impressively reduce weight gain in mice on a high-fat diet. Especially relevant is the fact that vitamin D levels made no difference in the weight of the animals.
In conclusion, non-burning sun exposure is vitally important to human health. If you would like to have a fat content that is less than others, be sure to obtain your share or sunshine and make weight-control for you and your children much easier!
[1] V. Daraki, T. Roumeliotaki, G. Chalkiadaki, M. Katrinaki, M. Karachaliou , V. Leventakou, M. Vafeiadi, K. Sarri, M. Vassilaki, S. Papavasiliou, M. Kogevinas and L. Chatzi. Low maternal vitamin D status in pregnancy increases the risk of childhood obesity. Pediatric Obesity Pediatr Obes. 2018 Jan 28. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12267. [Epub ahead of print]
Obesity: Do vitamin D and sunlight have a part? A new study shows that when vitamin D deficient pregnant women bear children, the children may become obese.[1] Furthermore, the children had larger waistlines at age 6, compared with children born to women who had sufficient vitamin D levels. The body-fat percentage of those born to vitamin D- deficient women was also significantly higher. Body fat-percentage is a measure of obesity (or lack thereof).
How is vitamin D produced?
The authors stated that 95% of vitamin D production in the body comes from sun exposure to skin. That is correct. Consequently, the expectant mothers spend too much time indoors. Or, they are frightened into sunscreen use, which can prevent production of 99% of vitamin D by sun exposure. Therefore, this type of obesity is a sun-deprivation disease. The research suggested that vitamin D supplements might be the answer. However, the answer is not supplements when sunlight is available. We should promote safe, non-burning sun exposure to prevent obesity.
Are there other studies regarding sunlight and obesity?
Much has been researched lately regarding the importance of sunlight in preventing obesity. In my last blog, I mentioned several of these studies: http://sunlightinstitute.org/staying-slim-sunlight/
Here is a list of the methods by which sun exposure helps to prevent or reverse obesity:
- First of all, because blue-spectrum light causes cells to dump part of their fat load, it helps weight-control
- Secondly, early-morning light, because it resets circadian rhythms, reduces the risk of weight-gain.
- Thirdly, exposure to ultraviolet radiation (one of the spectrums in sun exposure) has been shown to impressively reduce weight gain in mice on a high-fat diet. Especially relevant is the fact that vitamin D levels made no difference in the weight of the animals.
In conclusion, non-burning sun exposure is vitally important to human health. If you would like to have a fat content that is less than others, be sure to obtain your share or sunshine and make weight-control for you and your children much easier!
[1] V. Daraki, T. Roumeliotaki, G. Chalkiadaki, M. Katrinaki, M. Karachaliou , V. Leventakou, M. Vafeiadi, K. Sarri, M. Vassilaki, S. Papavasiliou, M. Kogevinas and L. Chatzi. Low maternal vitamin D status in pregnancy increases the risk of childhood obesity. Pediatric Obesity Pediatr Obes. 2018 Jan 28. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12267. [Epub ahead of print]
 Although liver cancer is generally thought to be related to drinking, other factor such as obesity, HIV infection, smoking, diabetes, socioeconomic factors, drugs and others come into play. A recent study compared sun exposure to liver cancer and adjusted for the aforementioned factors. Sun exposure was shown to be a major factor in reducing the risk of the most prevalent and deadly liver cancer, called hepatocellular carcinoma.[1]
Although liver cancer is generally thought to be related to drinking, other factor such as obesity, HIV infection, smoking, diabetes, socioeconomic factors, drugs and others come into play. A recent study compared sun exposure to liver cancer and adjusted for the aforementioned factors. Sun exposure was shown to be a major factor in reducing the risk of the most prevalent and deadly liver cancer, called hepatocellular carcinoma.[1]
Major finding for liver cancer:
The subjects were divided into five groups, or quintiles, based on their sun exposure. In addition such factors as as outdoor activity, geographical residence, urban or rural settings, etc. were adjusted for.
Most noteworthy, was the fact that for each quintile of increasing sun exposure, there was a 17% decrease in the liver cancer risk.
A disappointment:
The only disappointing part to the study was this: The researchers assumed that the positive influence of sun exposure on liver cancer was due to vitamin D production. And, they may have been correct. Yet the sun causes the body to produce many other photoproducts. Due to the sun’s myriad effects, serotonin, endorphin, BDNF, nitric oxide, and dopamine are all increased. Therefore, it is impossible to know if vitamin D alone was the reason for the reduced risk of liver cancer. However, vitamin D undoubtedly played a large part in the positive results. And, there is a problem with giving vitamin D the credit without knowing for sure. People may believe, due to this research, that they need only to take a vitamin D supplement to receive all benefits of sunlight. Therefore, they can make very bad assumptions.
This is the first study on sun exposure and liver cancer.
Probably, this is the first research to show a link between liver cancer and inadequate sun exposure. However, there are indications that sun exposure is associated with a reduced risk of another liver ailment, called fatty liver disease.[2]
In conclusion, if you are a liver lover, you can love your liver by protecting it from liver cancer. Hence, you should obtain your share of unscreened, direct, non-burning sun exposure. Happy sunning!
[1] Trang VoPham, Kimberly A. Bertrand, Jian-Min Yuan, Rulla M. Tamimi, Jaime E. Hart,
and Francine Laden. Ambient ultraviolet radiation exposure and hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in the United States. Environmental Health (2017) 16:89.
[2] Gorman S, Black LJ, Feelisch M, Hart PH, Weller R. Can skin exposure to sun prevent liver inflammation? Nutrients 2015 May 5;7(5):3219-39.
 Does cognitive loss lead to dementia? Yes. Is vitamin D important to the risk of cognitive loss? Yes. Do those levels also influence the ability to think (cognitive ability)? In 2002, 252 people were assessed for vitamin D levels, signs of dementia and cognitive ability.[1] And, in 2012 another assessment was completed. The data was then assessed to determine if the initial vitamin D levels were associated with different risks of dementia and cognitive ability after 10 years.
Does cognitive loss lead to dementia? Yes. Is vitamin D important to the risk of cognitive loss? Yes. Do those levels also influence the ability to think (cognitive ability)? In 2002, 252 people were assessed for vitamin D levels, signs of dementia and cognitive ability.[1] And, in 2012 another assessment was completed. The data was then assessed to determine if the initial vitamin D levels were associated with different risks of dementia and cognitive ability after 10 years.
Cognitive ability results:
First of all, those with higher vitamin D levels at the beginning of the ten-year period had about 40% better executive functioning at the end of the period compared with those who had lower vitamin D levels (executive functions are a set of processes that all have to do with managing oneself and one’s resources in order to achieve a goal, and they can be viewed as the “conductor” of all cognitive skills.)[2]
Of course, vitamin D levels are determined by the quantity of sun exposure one receives. Therefore, we could say that vitamin D levels are a surrogate measurement of sun exposure.
Other research on sunlight and cognitive ability:Much research has been done on the association of sun exposure on cognitive abilities, so this research is no surprise. Especially relevant are the results of more recent research, based on a 15-year residential history of varying degrees of sun exposure. It has also shown cognitive impairment in persons who were below the median exposure to sun was 88% greater than those who were above the median.[3] Researchers mentioned vitamin D as a possible mechanism by which sun positively influenced cognitive abilities. And, they also remarked that regulation of the circadian rhythm by sun could be a factor. Additionally, these same investigators had previously shown the following: lower levels of sun exposure resulted in a 2.6-times higher incidence of cognitive impairment.[4]
Does BDNF play a part in protecting cognitive ability?
Part of the reason for better cognitive skills under the influence of sun exposure may not have anything to do with vitamin D. It could be due to a chemical called Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). It is a part of a cascade of proteins promoting growth of neurons and preventing nerve death.[5] It is especially relevant that BDNF levels have been shown to increase significantly after bright light exposure.[6] And, in what I would consider to be a remarkably important study, both light exposure and treadmill exercise increased the expression of BDNF in rats.[7] And—as the researchers showed—exercise and/or bright light promoted neurogenesis (new nerve cell growth) in the adult rat brain. How important is this finding for adults who are worried about cognitive decline? Furthermore, we are actually seeing an example of new brain cells being built by bright light and exercise! Researchers have shown that BDNF has an effect on behavior, mood (e.g. depression), and brain adaptation (e.g. plasticity) and that its levels fluctuate seasonally in correlation with the amount of ambient sun:[8]
In addition, we can add one more natural chemical inversely associated with cognitive decline, depression, memory loss, and nervous system degeneration, and directly associated with sun exposure. We now have vitamin D, serotonin, endorphins, dopamine and BDNF. Hence, sun exposure is absolutely necessary to human health. Be sure you are obtaining your share! Don’t let your mind deteriorate due to avoiding the sunlight.
Embrace the sun, but do it safely. Finally: avoid sunburn.
[1] Alicia M. Goodwill, Stephen Campbell, Steven Simpson Jr, Maria Bisignano,
Cherie Chiang, Lorraine Dennerstein, Cassandra Szoekea. Vitamin D status is associated with executive function a decade later: Data from the Women’s Healthy Ageing Project. Maturitas 107 (2018) 56–62
[2] http://www.ldonline.org/article/29122
[3] Kent ST, Kabagambe EK, Wadley VG, Howard VJ, Crosson WL, Al-Hamdan MZ, Judd SE, Peace F, McClure LA. The relationship between long-term sun radiation and cognitive decline in the REGARDS cohort study. Int J Biometeorol. 2014 Apr;58(3):361-70.
[4] Kent ST, McClure LA, Crosson WL, Arnett DK, Wadley VG, Sathiakumar N. Effect of sun exposure on cognitive function among depressed and non-depressed participants: a REGARDS cross-sectional study. Environ Health. 2009 Jul 28;8:34
[5] http://scicurious.scientopia.org/2010/12/13/bdnf-and-depression/
[6] Tirassa P1, Iannitelli A, Sornelli F, Cirulli F, Mazza M, Calza A, Alleva E, Branchi I, Aloe L, Bersani G, Pacitti F. Daily serum and salivary BDNF levels correlate with morning-evening personality type in women and are affected by light therapy. Riv Psichiatr. 2012 Nov-Dec;47(6):527-34.
[7] Kwon SJ, Park J, Park SY, Song KS, Jung ST, Jung SB, Park IR, Choi WS, Kwon SO. Low-intensity treadmill exercise and/or bright light promote neurogenesis in adult rat brain. Neural Regen Res. 2013 Apr 5;8(10):922-9.
[8] Molendijk ML, Haffmans JP, Bus BA, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW, Prickaerts J, Oude Voshaar RC, Elzinga BM. Serum BDNF concentrations show strong seasonal variation and correlations with the amount of ambient sun. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48046.
Is the sunbed a Gianus Bifrons (two-headed god)?
Sunbeds, Good or bad?
Recent research comes to the conclusion that indoor tanning is a Gianus Bifrons,[1] which is interpreted as a two-headed god. One head, according to these researchers, is an increase in various skin cancers (a dubious claim). The other head is the ability of sunbeds to produce large quantities of vitamin D, increasing serum vitamin D concentrations up to two fold. In addition, this increase in vitamin D, they believe, could lead to a decrease in myriad diseases.
The authors of the paper state the following: “Therefore, some favorable effects [of tanning beds] against the risk of developing many human diseases, including non-skin cancers, cannot be excluded at first glance, although they may not be only linked to [higher] vitamin D status.” They also go on to suggest that more research should be performed to determine if the unfavorable effects of indoor tanning on skin cancers may be outweighed by the favorable benefits of amelioration of low vitamin D levels.
This research ignored many research studies showing that regular, non-burning sun exposure is protective against melanoma. In my upcoming book, Embrace the sun, about 14 different research studies are cited. All of these studies demonstrate a positive effect of sun exposure. There are also positive effects of sun exposure and sunbed exposure, beyond the ability to produce vitamin D. Nitric oxide (NO) is produced by both. NO is a vasodilator that lowers blood pressure and reduces the risk of heart disease.
No increase in melanoma!
Perhaps the most important study to differentiate between the positive effects and negative effects of sunbed exposure is this one: A 20-year Swedish study demonstrated that women who used sunbeds were 23% less likely to die from any cause than women who did not use them.[2] This study also showed no increase in melanoma after the 20-year period.
So, what more do we need to know about the pros and cons of sunbed use?
Here are a few more positive effects of sunbeds on human health:
- Sunbed use reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes.[3]
- Sunbed use strengthens bone.[4]
- Sunbed use controls psoriasis and eczema.[5]
- Sunbed use reduces chronic pain.[6], [7]
- Sunbed use may help unborn children.[8]
- Sunbed use reduces the risk of clots.[9]
- Sunbed use is associated with lower breast-cancer risk.[10]
- Sunbed use reduces the risk of death.[11]
[1] Giuseppe Lippi*, 1, Gianfranco Cervellin†, Elisa Danese. Indoor Tanning a Gianus Bifrons:
Vitamin D and Human Cancer. Advances in Clinical Chemistry 2017;20:1-16
[2] Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, Ingvar C, Nielsen K, Stenbeck M, Olsson H. Avoidance of sun exposure is a risk factor for all-cause mortality: results from the Melanoma in Southern Sweden cohort. J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;276(1):77-86.
[3] P.G. Lindqvist, H. Olsson, M. Landin-Olsson, Are active sun exposure habits related
to lowering risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women, a prospective cohort
study?, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 90 (2010):109-114.
[4] Tangpricha V, Turner A, Spina C, Decastro S, Chen TC, Holick MF. Tanning is associated with optimal vitamin D status (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration) and higher bone mineral density. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80:1645-49.
[5] Radack KP, Farhangian ME, Anderson KL, Feldman SR. A review of the use of tanning beds as a dermatological treatment. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015 Mar;5(1):37-51.
[6] Kaur M, Feldman SR, Liguori A, Fleischer AB Jr. Indoor tanning relieves pain. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2005 Oct;21(5):278.
[7] Taylor SL, Kaur M, LoSicco K, Willard J, Camacho F, O’Rourke KS, Feldman SR. Pilot study of the effect of ultraviolet light on pain and mood in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Altern Complement Med. 2009 Jan;15(1):15-23.
[8] Bukhari, M. Quoted in London Times April 27, 2008.
[9] Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Olsson H. Does an active sun exposure habit lower the risk of venous thrombotic events? A D-lightful hypothesis. J Thromb Haemost. 2009 Apr;7(4):605-10.
[10] Yang L, Veierød MB, Löf M, Sandin S, Adami HO, Weiderpass E. Prospective study of UV exposure and cancer incidence among Swedish women. J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;276(1):77-86
[11] Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, Ingvar C, Nielsen K, Stenbeck M, Olsson H. Avoidance of sun exposure is a risk factor for all-cause mortality: results from the Melanoma in Southern Sweden cohort. J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;276(1):77-86.
 Do sunbeds have healthful effects?The Vitamin D Society of Canada recently issued a significant news release: It describes new research reported on the vitamin D-producing effects of tanning salon sunbeds. The study was published in the journal DermatoEndocrinology,[1] and it found that standard tanning salon sunbeds are very effective in raising serum levels of vitamin D. Those who used the beds were able to attain optimal levels (more than 100 nmol/L) [40ngml] D during winter. Actually, another earlier study had also showed similar results,[2] so this research served to corroborate that finding.
Do sunbeds have healthful effects?The Vitamin D Society of Canada recently issued a significant news release: It describes new research reported on the vitamin D-producing effects of tanning salon sunbeds. The study was published in the journal DermatoEndocrinology,[1] and it found that standard tanning salon sunbeds are very effective in raising serum levels of vitamin D. Those who used the beds were able to attain optimal levels (more than 100 nmol/L) [40ngml] D during winter. Actually, another earlier study had also showed similar results,[2] so this research served to corroborate that finding.
The significance of this evidence about sunbeds cannot be overemphasized.
This is transcendentally important information for Canadians! They receive little or no vitamin D-producing sun exposure in winter. It is similarly important for all others who live at high latitudes, work indoors or are rarely exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D deficiency, primarily due to lack of sun exposure, is a disaster that becomes larger each year. The reason? The Powers of Darkness continue to promote sun avoidance and sunscreen use. It has been shown that an SPF 15 sunscreen will decrease sun-stimulated vitamin D production by up to 99.5%.[3]
The paper was written by Doctors Samantha Kimball, Jasmine Lee and Reinhold Vieth. Here is the research link: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19381980.2017.1375635
This new research builds on the importance of vitamin D health benefits: It found that if Canadians raised their vitamin D blood levels to an optimal 100 nmol/L, it could prevent 23,000 premature deaths. It could also save $12.5 Billion annually in direct health care costs. The researchers indicate that low vitamin D levels in winter leave one more susceptible to many diseases. Some of these include colds and flu. And, they also lead to more serious illnesses such as osteoporosis, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, many cancers and heart disease. Remember this, however: The sunbeds that emit Ultraviolet B (UVB) light are the only ones that should be used. UVB is necessary for the production of vitamin D. The high pressure beds produce little or no UVB. Therefore, I do not recommend them.
Due to the scare tactics of those who frighten the public out of the sunlight, many other facts about the beneficial effects of sunbeds have been forgotten or hidden. Below are a few more of those facts.
Healthful Effects of Sunbeds:
- Sunbeds strengthen bone. As mentioned above, one study compared 50 subjects who used a sunbed at least once weekly, to 106 control subjects who did not use them. Sunbed users had 90% higher vitamin D levels than non-users. They also had significantly higher bone-mineral density, indicative of stronger bones.[4]
- Sunbeds can control psoriasis and eczema. Research showed convincingly that sunbeds are a valid treatment for psoriasis.[5] And, it also stated another conclusion: Sunbeds could be useful “as a treatment option for atopic dermatitis [eczema], mycosis fungoides, acne, scleroderma, vitiligo, and pruritus, as well as other UV sensitive dermatoses.”
- Sunbeds use reduce chronic pain.[6], [7] A study of pain in fibromyalgia patients, conducted by dermatologists, revealed that those who used UV-producing sunbeds experienced a decrease of 0.44 points on a 10 point scale (Likert scale), when compared to those who did not receive UV light. Furthermore, feelings of well-being and relaxation were also reported among the tanners.
- Sunbeds may help unborn children. Sunbeds are now being recommended for use by pregnant women who will give birth in a winter month, in order to protect the unborn child from osteoporosis during adulthood.[8]
- Sunbed use reduces the risk of clots. In an eleven-year study of the sun-exposure habits of 40,000 women, venous thrombotic (clotting) events were measured. It was found that women who sunbathed during the summer, on winter vacations, or when abroad, or used sunbeds, were at 30% reduced risk of clots compared to those who did not sunbathe.[9]
-
Sunbed use is associated with lower breast-cancer risk.[10]
- Sunbed use reduces the risk of death. Finally, Perhaps the most important research on sunbeds was a 20-year study: it showed that women who used sunbeds were 23% less likely to die from any cause than women who did not use them. [11]
Due to the health benefits, and also due to the way they help my mood, I enjoy using sunbeds. Nevertheless, I am not telling you to use them or to avoid them. However, the aforementioned positive information should at least help you to make an informed decision. Stay healthy and remember that the sun is your friend!
[1] Samantha Kimball, Jasmine Lee and Reinhold Vieth. Sunbeds with UVB radiation can produce physiological levels of serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in healthy volunteers. Article: e1375635. Published online: 06 Oct 2017.
[2] Tangpricha V, Turner A, Spina C, Decastro S, Chen TC, Holick MF. Tanning is associated with optimal vitamin D status (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration) and higher bone mineral density. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80:1645-49.
[3] Matsuoka LY, Ide L, Wortsman J, MacLaughlin JA, Holick MF. Sunscreens suppress cutaneous vitamin D3 synthesis. .Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1987; 64:1165-68.
[4] Tangpricha V, Turner A, Spina C, Decastro S, Chen TC, Holick MF. Tanning is associated with optimal vitamin D status (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration) and higher bone mineral density. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80:1645-49.
[5] Radack KP, Farhangian ME, Anderson KL, Feldman SR. A review of the use of tanning beds as a dermatological treatment. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015 Mar;5(1):37-51.
[6] Kaur M, Feldman SR, Liguori A, Fleischer AB Jr. Indoor tanning relieves pain. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2005 Oct;21(5):278.
[7] Taylor SL, Kaur M, LoSicco K, Willard J, Camacho F, O’Rourke KS, Feldman SR. Pilot study of the effect of ultraviolet light on pain and mood in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Altern Complement Med. 2009 Jan;15(1):15-23.
[8] Bukhari, M. Quoted in London Times April 27, 2008.
[9] Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Olsson H. Does an active sun exposure habit lower the risk of venous thrombotic events? A D-lightful hypothesis. J Thromb Haemost. 2009 Apr;7(4):605-10.
[10] Yang L, Veierød MB, Löf M, Sandin S, Adami HO, Weiderpass E. Prospective study of UV exposure and cancer incidence among Swedish women. J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;276(1):77-86
[11] Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, Ingvar C, Nielsen K, Stenbeck M, Olsson H. Avoidance of sun exposure is a risk factor for all-cause mortality: results from the Melanoma in Southern Sweden cohort. J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;276(1):77-86.
Osteoarthritis is also known as wear-and-tear arthritis. Yet, the disease is not common in parts to the world where people work hard with their joints to make a living. Rather, the disease is relatively rare. Thus, we would not consider too much work to be the cause. One would think that all of that work with the joints would lead to more wear and tear, no? Osteoarthritis is characterized by bone and cartilage degeneration in joints. This leads to pain and joint stiffness and can lead to disability. 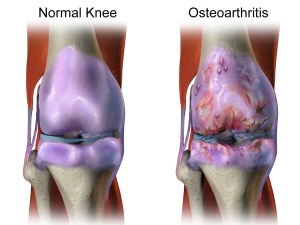
Vitamin D research.
Research has shown that those whose blood vitamin D measurements were in the middle and lowest thirds of serum vitamin D levels, had a threefold progression of osteoarthritis of the knee during a one-to-two year period. That is, when compared to those in the highest third. Low blood levels of vitamin D also predicted greater loss of cartilage in the joints.[1]
Other research demonstrates that in patients with arthritis of the knee, those with blood levels of vitamin D lower than 20 ng/ml (very low) have more disability. They also have more pain and more weakness than those with higher levels.[2], [3] Low vitamin D levels also correlate closely to greater knee pain and walking difficulty.[4]
Remember, unless it is stated that 25(OH)D levels are a result of supplementation or dietary sources, those levels are dependent on sun exposure. The research on osteoarthritis, discussed above, therefore, is really research on sun exposure.
Another horrific effect of arthritis.
Arthritic joints carry another devastating side effect. Hip replacement surgery is often prescribed for arthritic conditions: those people who go through total-hip-replacement procedures are 4.7 times as likely to have an ischemic stroke. They are also 4.4 times as likely to have a hemorrhagic stroke in the first two weeks post surgery.[5] Those stroke risks remain elevated for 6-12 weeks. The term “ischemic” means producing a local deficiency of blood supply by obstructing blood flow.
Sun exposure, therefore, has a protective effect against arthritis. Consequently, it has the potential to prevent hip-replacement surgery. In addition, it has the potential to prevent strokes.
Consider an article from the Express,[6] a UK online newspaper. It describes research published in the scientific journal, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases,[7]stating the following: “Millions of people could protect themselves from crippling arthritis by getting a regular dose of sunshine. Scientists found that women with the highest levels of exposure to the sun – specifically Ultraviolet B (UVB) light – were 21 per cent less likely to develop the disease.”
Safely embrace the sun, help prevent osteoarthritis and safeguard your health.
[1] McAlindonTE, Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Aliabadi P, Weissman B, Rush D, Wilson PW, Jacques P. Relation of dietary intake and serum levels of vitamin D to progression of osteoarthritis of the knee among participants in the Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med 1996;125:353-9.
[2] Baker K, Zhang YQ, Goggins J. Hypovitaminosis D and its association with muscle strength, pain and physical function in knee osteoarthritis (OA): a 30-month longitudinal, observational study; American College of Rheumatology meeting; San Antonio, TX; Oct 16-21, 2004; abstract 17552. Also see http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/538061
[3] Baker K, Zhang YQ, Goggins J. Hypovitaminosis D and its association with muscle strength, pain and physical function in knee osteoarthritis (OA): a 30-month longitudinal, observational study; American College of Rheumatology meeting; San Antonio, TX; Oct 16-21, 2004; abstract 17552. Also see http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/538061
[4] Wang, J., Nuite, M., Wheeler, L.M., Badiani, P., Joas, J., Mcadams, E.L., Fletcher, J., Lavalley, M.P., Dawson-Hughes, B., Mcalindon, T.E. 2007. Low Vitamin D levels are associated with greater pain and slow walking speed in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA). In: American College of Rheumatology Scientific Meeting, 11/6/07-11/11/07, Boston, MA. 56(9supplement): S124. Accessed May 14, 2010 at http://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publications.htm?SEQ_NO_115=211611
[5] Lalmohamed A, Vestergaard P, Cooper C, de Boer A, Leufkens HG, van StaaTP, de Vries F. Hip replacement surgery and stroke. Stroke 2012;43(12):3225-9.
[6] http://www.express.co.uk/life-style/health/375632/Sun-helps-stop-arthritis. (accessed November 27, 2015).
[7] Arkema EV, Hart JE, Bertrand KA, Laden F, Grodstein F, Rosner BA, Karlson EW, Costenbader KH. Exposure to ultraviolet-B and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women in the Nurses’ Health Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Apr;72(4):506-11
 New research from New Zealand shows that children who live in South Island of New Zealand have at least three times the risk of bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC)[1] when compared to those who live on the North Island. According to an article referencing this research, these bowel diseases usually appear in the pre-teen or teenage years and are incurable. The researchers believe that sun exposure and one of its photoproducts, Vitamin D, may play a part, although the low selenium content of the soil may also have an influence on bowel diseases.
New research from New Zealand shows that children who live in South Island of New Zealand have at least three times the risk of bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC)[1] when compared to those who live on the North Island. According to an article referencing this research, these bowel diseases usually appear in the pre-teen or teenage years and are incurable. The researchers believe that sun exposure and one of its photoproducts, Vitamin D, may play a part, although the low selenium content of the soil may also have an influence on bowel diseases.
In the southern hemisphere, of course, the farther south one travels, the colder and cloudier the weather becomes. Hence, the South Island has far less sun exposure than the North Island.
Although the researchers did not know for sure that the sunlight and vitamin D hypothesis was correct regarding bowel disease, their idea certainly has plenty to back it up. Crohn’s disease is closely correlated to vitamin D deficiency and winter season,[2] indicating an inverse relationship with sun exposure and vitamin D production. A study of female nurses in the US found that “compared with women residing in northern latitudes [in the northern hemisphere] at age 30, the multivariate-adjusted risk for UC for women residing in southern latitudes was less than half.”[3] Also, in a 12-year investigation of hundreds of thousands of bowel disease patients, hospitalizations, and prolonged hospitalizations, for both UC and CD were higher among those who had low sun exposure compared to those with very high sun exposure.[4]
It is important to understand that bowel disease causes malabsorption of nutrients in the gut, leading to diseases of malnutrition.[5] Vitamin D is one of the “nutrients” that may not be absorbed efficiently, and therefore sun exposure, not supplements, may be the only viable source of vitamin D for a person with bowel disease.
So for a healthy gut, sun exposure plays a vital role. Be sure to enjoy safe, non burning sun exposure whenever possible.
[1] http://www.radionz.co.nz/news/national/340048/shining-light-on-bowel-disease-rates
[2] Gilman J, Shanahan F, Cashman KD. Determinants of vitamin D status in adult Crohn’s disease patients, with particular emphasis on supplemental vitamin D use. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jul;60(7):889-96.
[3] Khalili H, Huang ES, Ananthakrishnan AN, Higuchi L, Richter JM, Fuchs CS, Chan AT. Geographical variation and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among US women. Gut. 2012 Dec;61(12):1686-92.
[4] Limketkai BN, Bayless TM, Brant SR, Hutfless SM. Lower regional and temporal ultraviolet exposure is associated with increased rates and severity of inflammatory bowel disease hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Sep;40(5):508-17.
[5] Margulies SL, Kurian D, Elliott MS, Han Z. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with intestinal malabsorption syndromes–think in and outside the gut. J Dig Dis. 2015 Nov;16(11):617-33.
